
Cybersecurity with ThreatMon’s in-depth assessment:
The cyber threat environment in 2024 was characterized by a significant increase in ransomware attacks, dark web operations, and data breaches aimed at essential industries globally. ThreatMon’s in-depth assessment provides essential understanding of these changing threats and highlights the necessity of strong cybersecurity practices.
In 2024, more than 37 billion records were compromised in several major breaches. The “Mother of All Breaches” (MOAB) in January leaked over 28 billion records, revealing confidential data from services such as LinkedIn and Tencent. Other significant events comprised the National Public Data (NPD) Breach in August, impacting 2.9 billion records, and the Bank of America breach, which compromised financial information for 57,000 clients. These incidents emphasize weaknesses in external services and the essential requirement for secure supply chains.
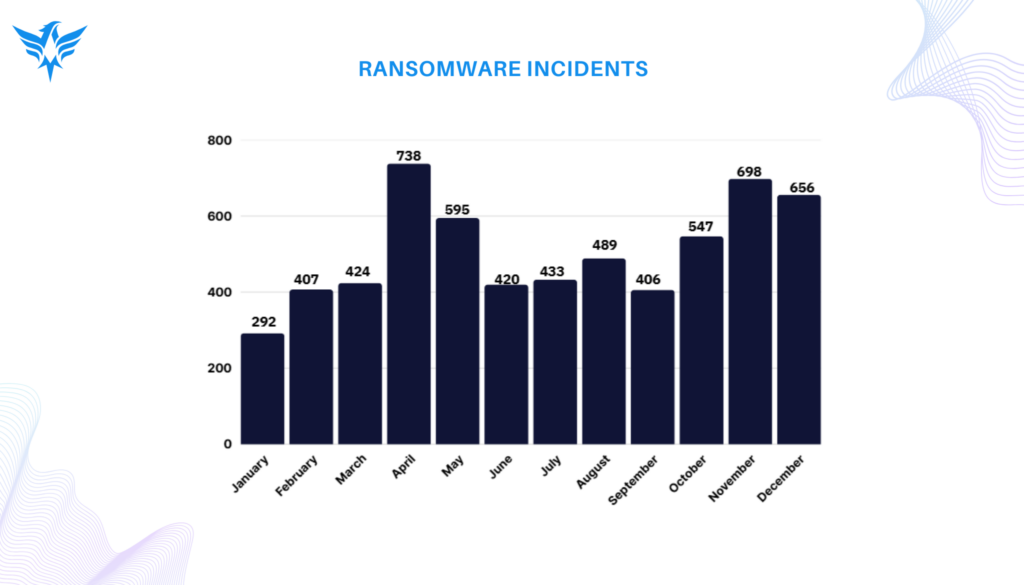
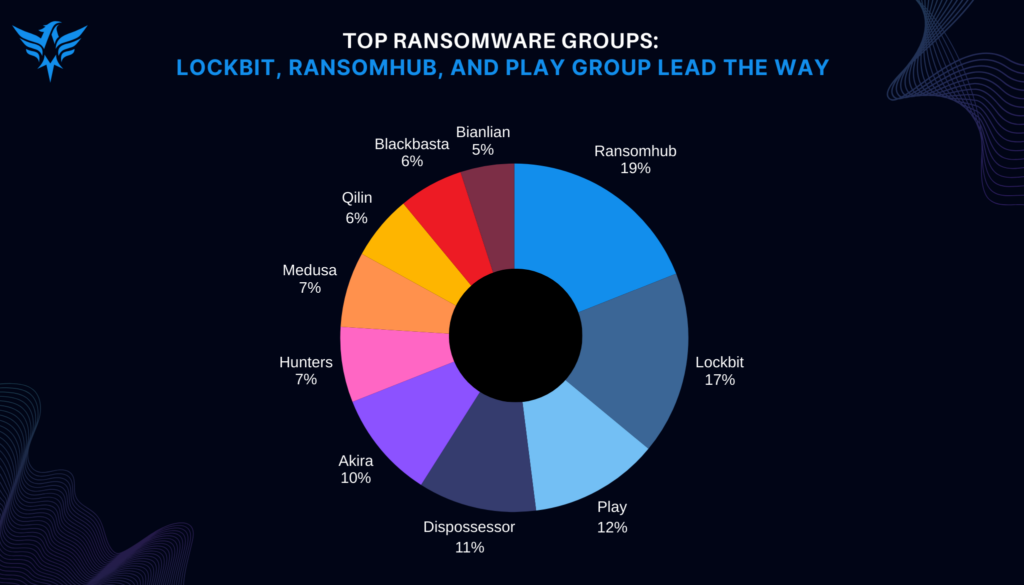
Ransomware assaults remained the primary concern in the threat landscape, with more than 6,100 cases documented. The healthcare and finance industries experienced a notable increase in attacks, together accounting for 20% of incidents. Prominent ransomware groups including RansomHub, LockBit, and Play utilized sophisticated methods such as double extortion and supply chain breaches to assault organizations. The United States, representing 63% of worldwide ransomware occurrences, continues to be the most impacted nation.
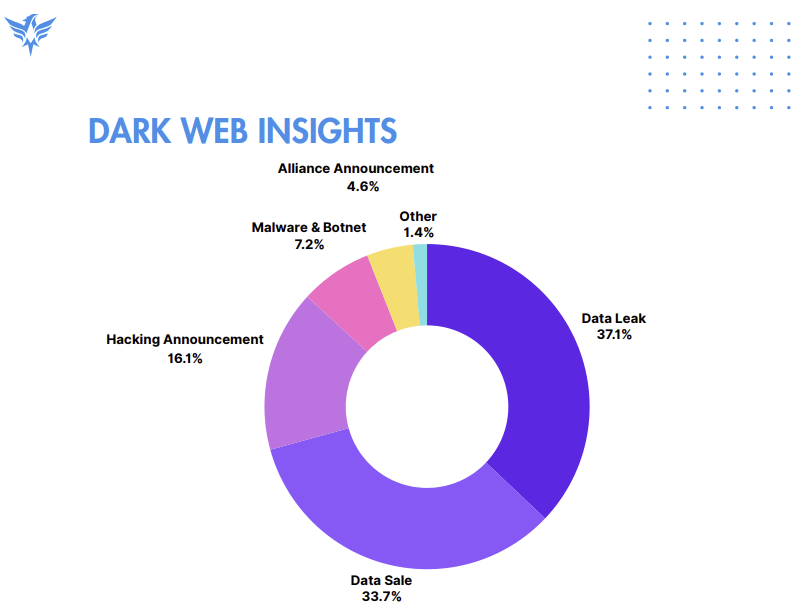
The dark web continued to serve as a focal point for harmful activities, logging more than 1,600 significant incidents in 2024. Data leaks (37%) and data sales (34%) were prevalent, highlighting the dark web’s influence in enabling cybercrime. Malicious actors often focused on the healthcare and finance industries, taking advantage of obsolete systems and vulnerabilities in third-party services. The United States was at the forefront of dark web activity, with the Russian Federation and India trailing behind.
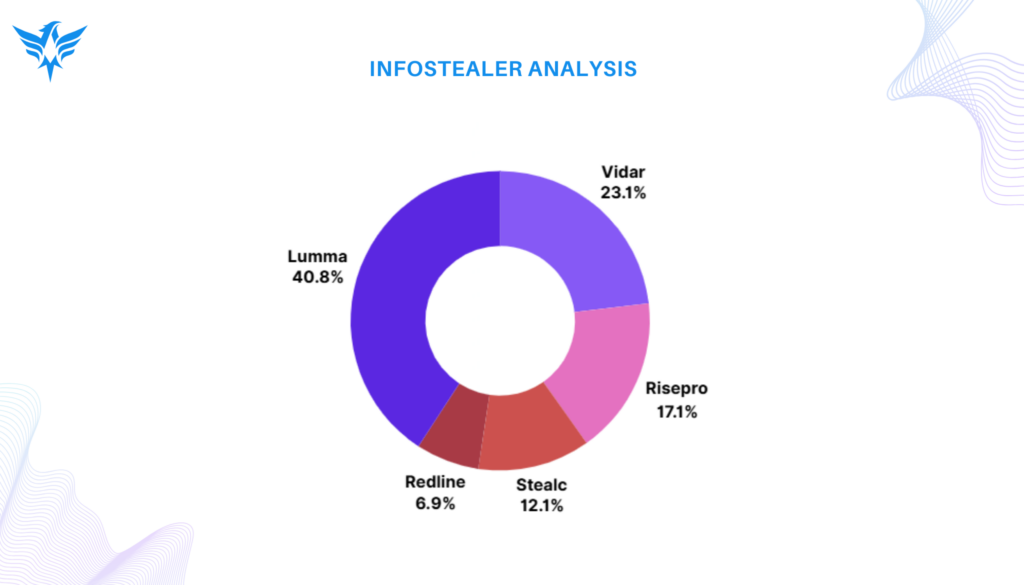
Stealer malware continued to evolve, with Lumma, Vidar, and RisePro leading the top threats. These malware strains targeted sensitive credentials and financial data, adapting their tactics to evade detection. The rising prominence of newer strains like Lumma emphasizes the need for continuous monitoring and adaptive defenses.
Exploited vulnerabilities remained a significant concern in 2024. Notable incidents included the Polyfill JS attack, which injected malware into over 100,000 websites, and vulnerabilities like CVE-2024-0012 and CVE-2024-9474, which enabled privilege escalation and unauthorized access. Organizations must prioritize patching and real-time vulnerability management to mitigate risks.
Below is a visual representation of some key data points from the report:
The 2024 Global Cyber Threat Report demonstrates the increasing sophistication and collaboration among threat actors. As the digital threat landscape grows more complex, organizations must adopt proactive measures, such as: