
AzzaSec Ransomware, developed by the AzzaSec Hacktivist Group, represents a significant cybersecurity threat due to its sophisticated features and destructive capabilities. This ransomware is particularly dangerous because of its fully undetected (FUD) nature and its use in targeted attacks via ransomware as a service (RaaS).
Development and Affiliations:AzzaSec Ransomware was developed by the AzzaSec Hacktivist Group, known for its financial motivations and opposition to Israel and Ukraine. They are allied with Russian groups Noname057(16) and APT44.
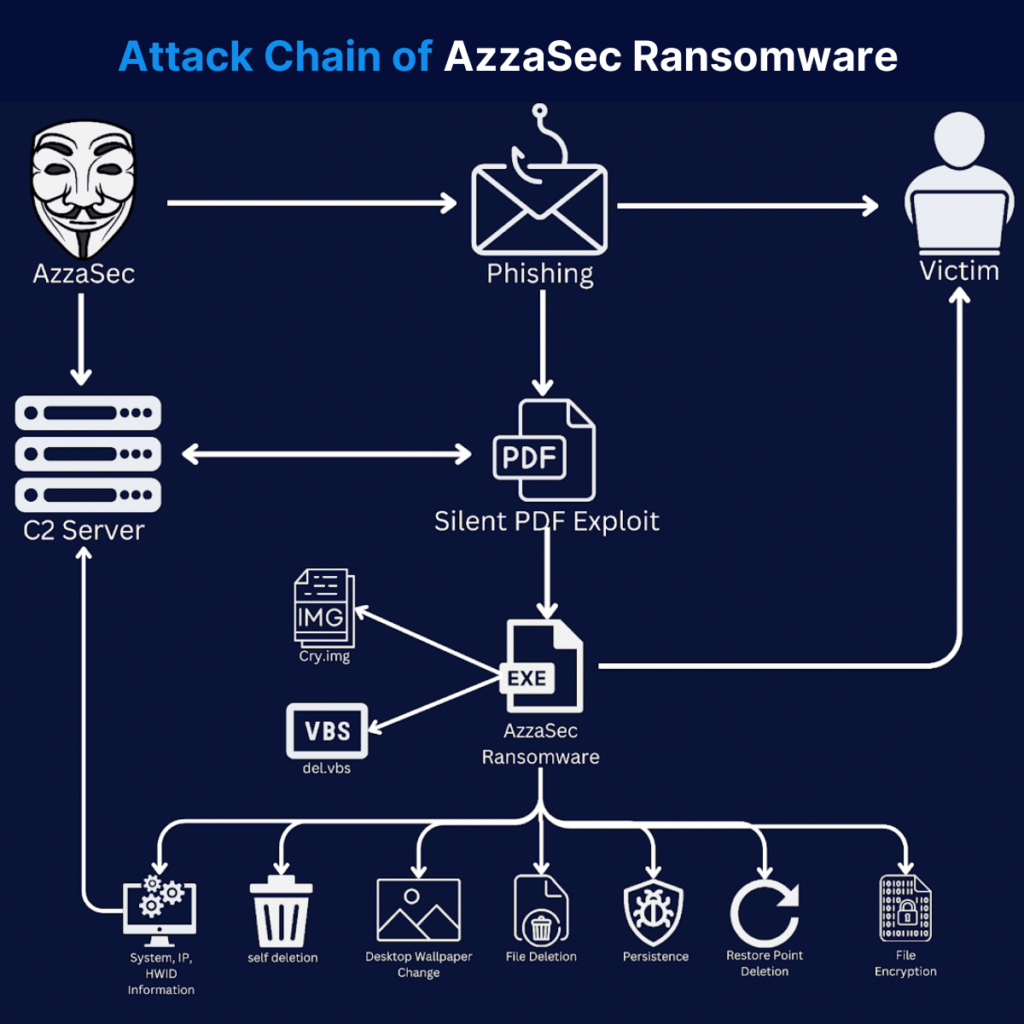
Infection Methods: Ransomware is disseminated through two primary methods: compromising remote Windows servers and phishing attacks utilizing a PDF dropper.
Encryption Details: Once infected, the Ransomware encrypts files with the AzzaSec_Encryptor extension using AES encryption and SHA512 to generate keys and IVs. It targets 120 different file formats.
Anti-Detection Capabilities: Ransomware features Anti-VM, Anti-Hosting, Anti-Sandboxing, and Anti-Debugger mechanisms to evade security measures.
Persistence and Extortion: To ensure persistence, the Ransomware places itself in the Startup directory, demanding a $600 payment for decryption. It also changes the system’s background and plays a menacing audio message to pressure victims into paying the ransom.
Initial Compromise: Involves social engineering through phishing emails with malicious PDF attachments.
Execution: PDF dropper executes commands via Foxit PDF Reader to download and run the Ransomware
Persistence: Ransomware copies itself to the Startup directory.
Encryption:Encrypts files and modifies system settings to prevent recovery.
Foundation: February 28, 2024, Italy-based.
Activities: Includes ransomware attacks, DDoS attacks, exploiting site and server vulnerabilities, and data leaks.
Notable Members: Walter Bishop, Friendied, and NoCry/Dmitry.Ransom.
Development: Created using VB .NET, 10MB in size.
Detection Rate: Low detection rate (1/40 on KleenScan).
Communication: Connects to a Command and Control (C2) server for decryption keys and monitoring compromised systems.
Unpacking: The Ransomware is packed with .NET Reactor and unpacked using Net Reactor Slayer.
Dynamic Analysis: Analyzes network connections to detect C2 communications and encrypted file extensions.
Static Analysis: Reveals the use of AES encryption and SHA512 hashing for key and IV generation.
AzzaSec Ransomware is a potent and evolving threat, necessitating robust cybersecurity measures and vigilant monitoring to mitigate its impact. Through detailed analysis and reverse engineering, encrypted files can be recovered, and the Ransomware’s persistent attempts to compromise systems can be thwarted.
For more information, read the AzzaSec Ransomware Technical Malware Analysis Report.