
Understand why attack surface management is crucial for organizations, focusing on how it helps identify, monitor, and secure exposed assets to mitigate potential cyber threats.
Today, with the transition of organizations from traditional business processes to digital business processes, the likelihood of organizations facing the risk of cyber attacks on their digital assets is increasing. This situation brings with it the need for continuous management and monitoring of digital assets. Although the increase in the organization’s digital assets expands the cyber attack surface, it is possible to dominate digital assets with the right attack surface management solutions. The right Attack Surface Management solutions define the attack surfaces that organizations have, detect security threats on the attack surface and provide recommendations to eliminate threats.
An attack surface is a term used in the field of cybersecurity to describe the set of potential points of vulnerability that can be targeted by an attacker. It refers to all of the ways that an attacker might gain unauthorized access to a system, network, or application, and includes anything that might provide an opportunity for an attacker to exploit a weakness or vulnerability.
In simple terms, an attack surface can be thought of as the sum total of all the ways that an attacker might be able to access, manipulate, or disrupt a system. This can include things like software vulnerabilities, misconfigured systems, weak passwords, unpatched software, and much more. Anything that provides an opportunity for an attacker to gain access to a system or data can be considered part of the attack surface.
Understanding the concept of an attack surface is important because it helps security professionals and organizations identify potential vulnerabilities and take steps to mitigate them. By understanding the different ways that an attacker might try to gain access to a system, measures can be implemented that make it more difficult for attackers to succeed.
reducing the attack surface might involve implementing strong passwords, keeping software up to date, regularly testing and patching systems for vulnerabilities, and limiting access to sensitive information. By doing these things, the attack surface is reduced, making it more difficult for attackers to access systems or data.
It’s worth noting that the attack surface is not a fixed thing. As technology evolves and new threats emerge, the attack surface can change over time. For example, the widespread adoption of cloud computing has created new opportunities for attackers to target cloud-based systems, and so the attack surface has expanded to include new types of vulnerabilities.
In summary, the attack surface refers to the sum total of all the potential ways that an attacker might be able to gain access to a system, network, or application. By understanding the attack surface and taking steps to reduce it, organizations can improve their cybersecurity posture and make it more difficult for attackers to succeed.
Attack Surface Management (ASM) is a cyber security management service that an organization uses to manage and protect its digital attack surfaces. ASM is used to detect, analyze, report, and manage all assets in an organization’s computing infrastructure and all access points on their digital attack surfaces. As the digital presence of organizations on the internet increases, their attack surface increases at the same rate. This makes the attack surface management more and more difficult. When the attack surface reaches an uncontrollable size, the organization can be seriously damaged by attackers. With Attack Surface Management, continuous monitoring is performed on the attack surfaces that need to be managed, and each digital asset is subjected to security assessment. As a result, ASM detects, reports, and resolves security problems on the attack surface. In this way, the uncontrollability caused by the growth of the attack surface is eliminated.

ASM is critical for cyber security. These services detect assets, access points, risks, and vulnerabilities on organizations’ digital attack surfaces. In this way, organizations become more prepared against digital attacks.
ASM works using many different technologies. These technologies include vulnerability scanning tools, network scanners, web application security scanners, threat intelligence platforms, and artificial intelligence. With these technologies, ASM services detect all assets in customers’ digital attack surfaces, identify vulnerabilities, and provide recommendations to mitigate risks.
ThreatMon is a leading cybersecurity company in ASM (Attack Surface Management) services. By continuously monitoring organizations’ digital attack surfaces, ASM helps them identify potential risks, remediate vulnerabilities, and protect themselves from cyberattacks. ASM also helps clients become more cybersecurity aware and better prepared for cyberattacks.
ASM is an important step in cybersecurity. By utilizing ASM services for the management of digital attack surfaces, organizations create a more secure environment against cyber-attacks. ASM helps pinpoint an organization’s digital attack surface and provides the data needed to strengthen its defense mechanisms.
ASM services also help clients set an appropriate security policy. This policy includes strategies to identify vulnerabilities, mitigate risks, and protect organizations from cyber-attacks. ASM helps organizations become more cybersecurity aware and better prepared for cyberattacks.
Attack Surface Management (ASM) is a proactive security approach that involves identifying, analyzing, and mitigating the vulnerabilities in an organization’s digital infrastructure. The process typically involves the following steps:
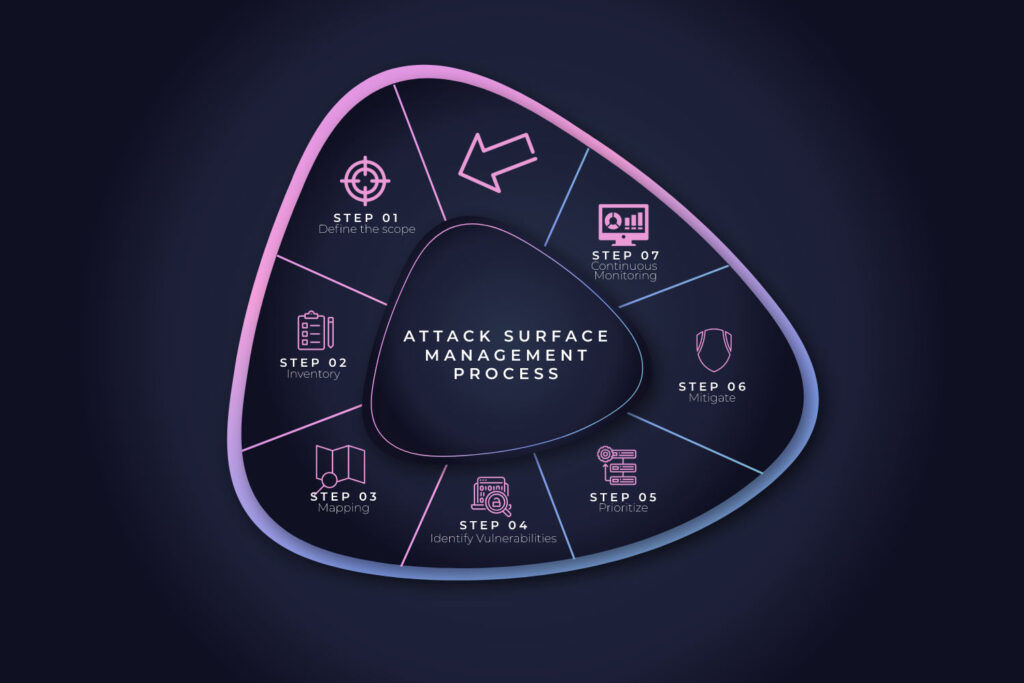
The first step is to define the scope of the ASM process, which includes identifying all the assets and systems within the organization that could be vulnerable to cyber-attacks.
The next step is to inventory all the assets identified in the previous step. This inventory should include hardware, software, data, and people and should be as comprehensive as possible.
Once an inventory of assets has been completed, the next step is to map out how the assets are connected and how they are used. This mapping process helps identify potential attack vectors and weaknesses in the system.
After mapping the assets and their connections, the next step is identifying potential system vulnerabilities. This can be done through various techniques, including vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and threat modeling.
Once vulnerabilities have been identified, they should be prioritized based on their severity and potential impact on the organization.
The final step is to mitigate the identified vulnerabilities. This may involve implementing technical controls, such as patches and software upgrades, or non-technical controls, such as employee training and awareness programs.
Once the initial ASM process is complete, it’s important to continuously monitor the attack surface to identify any new vulnerabilities that may arise as the organization’s infrastructure changes or evolves.
Overall, ASM is an ongoing process that requires regular attention and updates to ensure the organization’s digital infrastructure remains secure.
Today, organizations use digital assets extensively when organizing their business. This use of digital assets requires organizations to ensure their security to prevent hacking incidents. When attackers target an organization, they search for security problems in digital assets to achieve their damaging goals. These security problems appear as different threats.
Zero-day exploits refer to vulnerabilities in software or hardware that are unknown to the vendor and have not been patched. Attackers can exploit these vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to a system or steal sensitive information.
Incorrect or incomplete configuration of solutions used externally can expose organizations to some security problems such as Improper file and directory permissions, Administrative accounts with default passwords
These attacks are carried out by attacks from multiple sources to load heavy traffic on the network or overload services. Such attacks can block access to websites, causing service interruptions.
Security vulnerabilities occur in situations where information security measures are missing or insufficient, such as software errors, configuration errors, and outdated software.
APTs are sophisticated attacks typically carried out by nation-state actors or other well-funded organizations. APTs are designed to remain undetected for long periods, allowing the attackers to gather sensitive information or access critical systems.
Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in IoT devices to gain access to an organization’s network, steal sensitive data or launch DDoS attacks.
Cloud service providers are responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure, but organizations are still responsible for securing their own data and applications in the cloud. Failure to do so may result in data breaches and other security incidents.
ThreatMon identifies organizations’ attack surface due to its extensive asset discovery studies. ThreatMon classifies the identified attack surface data.
ThreatMon detects potential security threats that are present on the defined attack surface and are thought to have devastating consequences in the future. It uses the most up-to-date security research mechanisms when detecting security threats on the attack surface. As soon as a new threat appears on the attack surface, the threat is identified, and a security notification is generated to take action. ThreatMon performs AI-powered Attack Surface Management to detect threats that do not exist yet.
ThreatMon combines Attack Surface Management processes with Cyber Threat Intelligence to provide brand protection and digital risk protection for its business partners. For ThreatMon Cyber Threat Intelligence & Attack Surface Management services, you can request a demo at [email protected]