
Digital War in the Middle East: Cyber Threats in Israel-Iran Conflict
During the past few years, the chronic military and political dimensions of the conflict between Israel and Iran have progressively taken on aspects of cyber warfare. This new battle arena involves state-sponsored groups and hacktivists targeting both countries’ critical infrastructure, financial systems, and public opinion.
| Cyber Fattah Team | Anonymous Iran |
| 7 October Union | РУССКИЙ ЗАДАЧА СИЛА | РТФ |
| Z-BL4CX-H4T | VoltActivist |
| Team Ahadun-Ahad | {DEDSEC MUSLIMS} | Khilafah H4ckers |
| Anonymous Arabs | Noname057(16) |
| High Society | UserSec |
| Holy League | DEFACER INDONESIA |
| SYLHET GANG-SG | MaghrebSec |
| GhostSec | Black Maskers Army |
| Anonymous Guys | AnonymousActivist |
| Silent Cyber Force | Sumatra Selatan Cyber Team |
| Ghost Of Gaza | Anonymous Muslims |
| CyberDragon | Hacker Council Global |
| DXPLOIT | Al Ahad |
| Moroccan Black Cyber Army | CRYPTO CORP |
| Pro-Palestine Hackers Movement | Keymous |
| LAPSUS$ | DoubleFace |
| KillSec | RipperSec |
| RCH-SEC | Team 1945 |
| Team insane Pakistan | Moroccan Dragons |
| LulzSec Black | Evil of Anti ddos |
| Anonymous Collective | Alixsec |
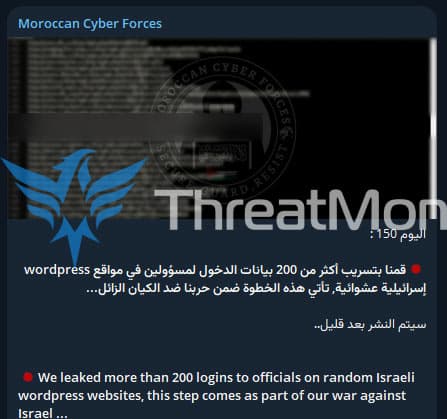
In the activity on Telegram detected by our team, the threat actor named “Moroccan Cyber Forces” claims to have leaked more than 200 login credentials of officials on Israeli WordPress websites.
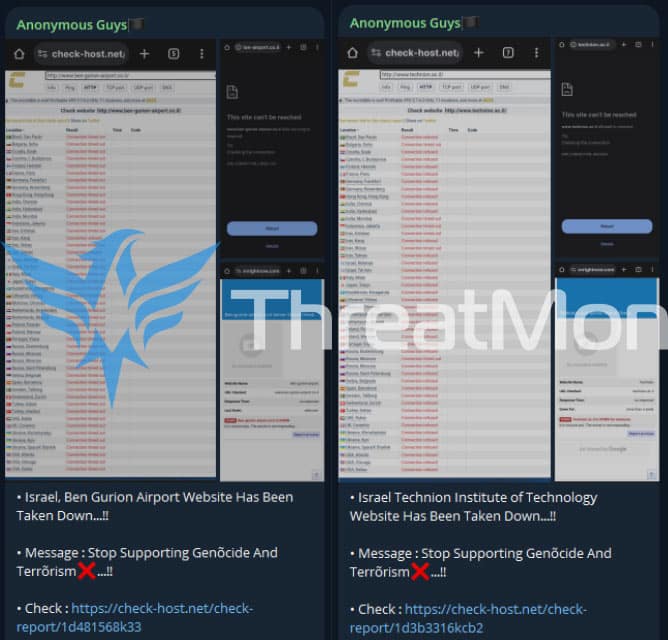
In an activity on Telegram detected by our team, a threat actor named “Anonymous Guys” targeted Ben Gurion International Airport, an international airport in Israel, and the Technion Institute of Technology in Israel. As a result of the DDoS attack, the websites became unavailable for a while.
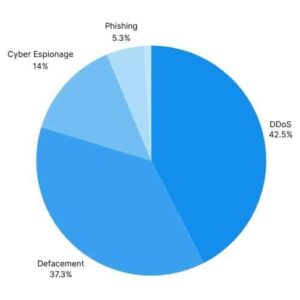
DDoS Attacks (%42.5): Pro-Iranian groups frequently use Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks against Israeli online services. These attacks involve sending massive traffic to make targeted websites temporarily inaccessible.
Website Defacement (%37.3): Groups supporting Iran may make unauthorized changes to the appearance or content of a targeted website. These changes are usually made to the site’s homepage and include a page with the attackers’ message or intent.
Cyber Espionage and Information Collection (%14): Pro-Iranian groups may engage in cyber espionage to collect sensitive data from specific individuals or organizations.
Phishing Attacks (%5.3): In some cases, pro-Iranian organizations may resort to phishing attacks to obtain sensitive information from targeted groups or individuals. In April 2024, APT42 appears to have intensified targeting users located in Israel.
Social Engineering and Ransomware (%1): Pro-Iranian groups use social engineering tactics to achieve their goals. They may also use ransomware to harm their targets or steal information.
| GlorySec | WeRedEvils |
| KromSec | S1L3NT_0N3 |
Four different groups supporting Israel are mobilizing against Iran’s influence. Each group has different motivations and strategies, and these groups are launching cyber attacks targeting Iran. As an extension of the war on the digital front, these groups are taking the conflict to the virtual world, targeting Iran’s infrastructure and sensitive systems.
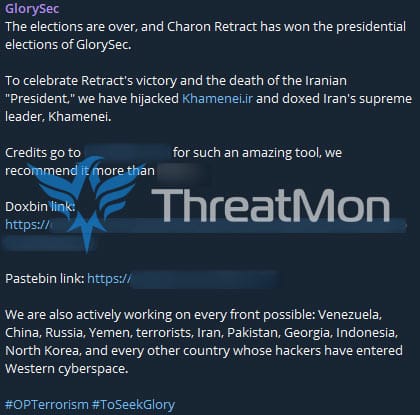
According to a detected telegram activity, GlorySec claims to have breached Khamenei, the official website of Ali Khamenei, Iran’s supreme religious and political leader and leaked Ali Khamenei’s information as a result of the breach.
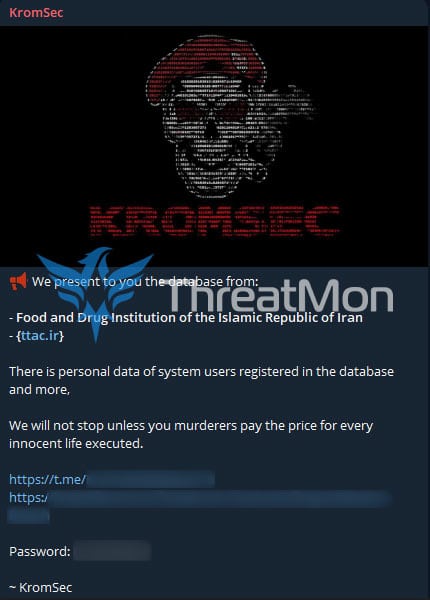
According to a detected telegram activity, KromSec claims to have leaked the Islamic Republic of Iran’s Food and Drug Administration database. The database allegedly contains the personal data of registered system users and more.
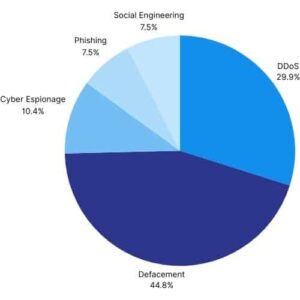
Website Defacement (44.8%): Groups supporting Israel may make unauthorized changes to the appearance or content of a targeted website. These changes are usually made to the site’s homepage and include a page with the attackers’ message or purpose.
DDoS Attacks (%29.9): Pro-Israel groups have been using Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks against Iranian online services. These attacks involve sending massive traffic to make targeted websites temporarily inaccessible.
Cyber Espionage and Information Collection (%10.4): Pro-Israel groups may engage in cyber espionage to collect sensitive data from specific individuals or organizations.
Social Engineering and Ransomware (%7.5): Pro-Israel groups use social engineering tactics to achieve their goals. They may also use ransomware to harm their targets or steal information.
Phishing Attacks (%7.5): In some cases, pro-Israel organizations may resort to phishing attacks to obtain sensitive information from targeted groups or individuals
The ongoing cyber warfare between Israel and Iran represents a digital extension of their physical conflict, with severe implications for both nations’ security and stability. As the cyber battlefield evolves, the sophistication and impact of these attacks are expected to grow, making cyber defense a critical component of national security for both Israel and Iran.
Digital War in the Middle East: Cyber Threats in Israel-Iran Conflict Report has been one of the most crucial, really describing the dynamic nature of cyber war in the Middle East and the need for strong cybersecurity with growing digital threats.
For more insights and intelligence on emerging cyber threats, contact ThreatMon, a leading platform providing comprehensive threat intelligence solutions.
Stay informed and stay secure in the digital world.