Cyber threat intelligence is a crucial aspect of cybersecurity and is becoming increasingly important as threats evolve and become more sophisticated. In this content, prepared by ThreatMon experts, we will explore cyber threat intelligence and its benefits to organizations and provide an overview of threat intelligence platforms. Businesses need to understand that relying solely on incident response, firewalls, and antivirus tools is no longer enough. With a comprehensive analysis and preventive measures obtained through threat intelligence, businesses can protect themselves from the financial losses and reputational damage that can result from cyber threats. An integrated cyber threat intelligence platform that leverages developing technology can provide proactive defense against rapidly increasing cyber threats.
Defining Cyber Threat Intelligence
Cyber threat intelligence is identifying, analyzing, and inferring cyber threats. The data collected goes through a processing process to ensure its accuracy and is then analyzed by experts. Using cyber threat intelligence, organizations can make faster and more informed cyber security decisions. With cyber threat intelligence, cyber defenders can take preventive measures before the attack and stop the attacker’s progress before exploitation. This includes various components such as threat intelligence, threat streams, endpoint security solutions, integration with SIEM and other security tools, and proactive defense against emerging threats.
Importance of Cyber Threat Intelligence for Organizations
Threat intelligence is of great importance in the cyber security world, and its significance can be divided into the following headings:
Data Loss Prevention
Cyber threat intelligence offers new-generation proactive solutions to organizations. Thanks to threat intelligence and analysis, data breaches can be completely prevented, and post-incident financial costs can be significantly reduced. Cyber threat intelligence prevents data breaches in your business as a result of comprehensive controls with IP addresses, domain names, external sources, and various deep analysis techniques that try to access your business.
Guidance on Security Measures
With threat intelligence, organizations scan and share cyber threats to strengthen their cyber defense posture. By sharing information about threats and vulnerabilities, an organization can use this information to identify new strategies, threat detection techniques, and mitigation methods in its defense system. Combining information from different sources enriches existing data. At ThreatMon, we analyze organizations that are under threat sectorally and geographically with the information and reports we share and aim to increase the cyber awareness of companies.
Information for Other Businesses and Individuals
Threat intelligence involves the use of information to understand the potential dangers and threats that an organization or person may face in the cybersecurity world. The information used for threat intelligence can be obtained from a variety of sources. If we want to examine the information obtained:
- Cyber threat types,
- Attack methods and tactics used,
- Identification of the attacker(s),
- Targets of attacks,
- Geographical assessments of attacks,
- Malware and signatures used in attacks,
- Vulnerabilities and existing weaknesses,
- Indicators of security breaches (IOCs).
Organizations can develop a solid preventive defense against the most destructive attacks with the information obtained. Sharing this information accurately and quickly enables other organizations and communities to be prepared for cyber threats. As ThreatMon, we are actively sharing IoC and C2 data in our GitHub account. IoC and C2 are offered free of charge by ThreatMon can be accessed via the GitHub link below.
Click here for the IoC list!
Click here for Daily Command and Control (C2) Feeds!
In-depth Cyber Threat Analysis and Reports
With cyber threat intelligence, a large number of data on previous and current attacks are collected. Meaningful conclusions are drawn from this collected information. Possible attack scenarios and methods related to your company can be analyzed. Thus, the attack can be prevented before it occurs. The information obtained as a result of previous attack methods provides an effective insight for your security tightening. In addition, cyber threat intelligence reports provide detailed and important information to businesses and individuals.
How Do Different Teams Benefit from Cyber Threat Intelligence
The information obtained as a result of Cyber Threat Intelligence research is effective and important in strengthening an organization’s cybersecurity posture by providing insight into potential threats and vulnerabilities. For this reason, different teams collaborate with cyber threat intelligence.
- Security Operations Center (SOC)
- Incident Response Team
- Threat Hunting Teams
- Cooperation with External Partners

- Security Operations Center (SOC)
When the information obtained by CTI is shared with SOC teams, it provides a proactive approach to identifying and countering future threats and examining cyber attacks.
- Incident Response Team
CTI and IR teams come together and provide a structure that makes sense of the “what” and “how” of the attack.
- Threat Hunting Teams
With threat hunting, potential threats in an organization’s digital infrastructure are actively scanned and combined with CTI, which provides proactive threat hunting.
- Cooperation with External Partners
Accurate information obtained as a result of CTI is shared with external partners, and the overall cyber posture is strengthened. CTI teams collaborate with the teams mentioned above to develop a robust and rapid defense in the cyber environment.
General Terms About Cyber Threat Intelligence
Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) is the process of collecting and analyzing information about current and potential attacks that threaten an organization’s or its assets’ security.
Threat Actor: A threat actor is the person or persons responsible for an attack. They can be cyber criminals, hacktivists, nation-states, and insiders.
Indicators of Compromise (IoC): IoC obtained during or after a cybersecurity incident is used as a clue and evidence of a data breach. Thanks to IoC, finding the tools used in the attack and even the person behind it is possible.
Malware: Malware is any malicious software, code, or program designed to harm systems. For example, there are different types of viruses, worms, ransomware, etc.
Phishing: Phishing is an attack method in which sensitive information is obtained by tricking people with social engineering techniques.
Exploit: Exploit is a technique or piece of code used to exploit a vulnerability in a system or application.
APT: APT stands for Advanced Persistent Threat. It is a strategically targeted cyber-attack in which the threat actor gains access to a network and remains on the web for an extended period. Advanced Persistent Threat Groups (APTs) are commonly known as state-sponsored cybercrime organizations. These groups use cyberattacks with the intent to harm a variety of targets, such as utilities, companies, government agencies, and the defense industry.
TTP: TTP refers to technique, tactics, and procedure. Technique refers to the attack methods used by attackers to infiltrate a specific target. Tactics describe the attackers’ goals and strategies. The procedure describes how attackers apply techniques and tactics.
OSINT: OSINT is intelligence obtained from publicly available sources such as websites, social media, and public sources. The data obtained through open-source intelligence contains valuable information that can help us understand potential cyber threats.
Dark Web: The Dark Web is a part of the internet that cannot be accessed with standard browsers and where illegal activities that pose a risk to access are intense. Threat actors use the dark web to buy and sell hacking tools, data breaches, and stolen information. It is usually accessed using specialized software; the best known is called Tor (The Onion Router).
Incident Response: Incident response is the procedures and technologies used to detect cyber threats, security breaches, or cyber-attacks related to an organization.
Command and Control (C2): Command and control is the infrastructure that attackers use to communicate with and control compromised systems.
Types of Cyber Threat Intelligence
There are four different types of cyber threat intelligence: strategic, tactical, technical, and operational. These four different types contain inseparable and complementary information for vital cyber intelligence.

Strategic Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI)
Strategic intelligence is used to identify who the actors behind attacks are and is used by senior decision-makers. This involves understanding the motivations of attackers and learning from previous incidents. It reveals the attackers who are likely to target and their motives. Analyze attacker profiles that attack other organizations in the same sector. Sectoral inferences are used to calculate the likelihood of the organization being targeted, thus creating a risk profile. Measures to be taken to reduce the risk profile are determined. Having such information provides insight into future attacks and tactics.
Tactical Cyber Threat Intelligence
Tactical cyber threat intelligence is a type of intelligence that includes technical and detailed analysis of cyber threats encountered during daily cybersecurity operations. Technical details include information on attack methods, malware, and vulnerabilities. It also includes indicators (IoCs) that can be used to detect attacks.
Technical Cyber Threat Intelligence
Technical threat intelligence adopts a structure that focuses on the techniques of threat actors and the threats that may occur.
Operational Cyber Threat Intelligence
Operational threat intelligence aims to understand the capabilities of adversaries. It is not enough for organizations to know who the enemy is; being aware of what the enemy is capable of provides an important context for security incidents.
Use Cases of Threat Intelligence Solution
Incident Response
The goal is to minimize potential damage and reduce the time and cost required to repair damage following an attack. Cyber threat intelligence collects extensive data to achieve this goal. It aims to prevent incidents by identifying existing vulnerabilities, detecting external assets, and collecting sensitive data on the web.
Vulnerability Management
A vulnerability refers to a situation where a system or application is unprotected. It can allow an attacker to gain unauthorized access and cause unintended service use. Vulnerabilities can have many different causes. Factors such as software bugs, weak encryption, malware infection, and lack of updates and patches lead to vulnerabilities. With cyber threat intelligence, vulnerabilities are detected, existing weaknesses are identified and organizations are informed continuously and at the earliest possible time.
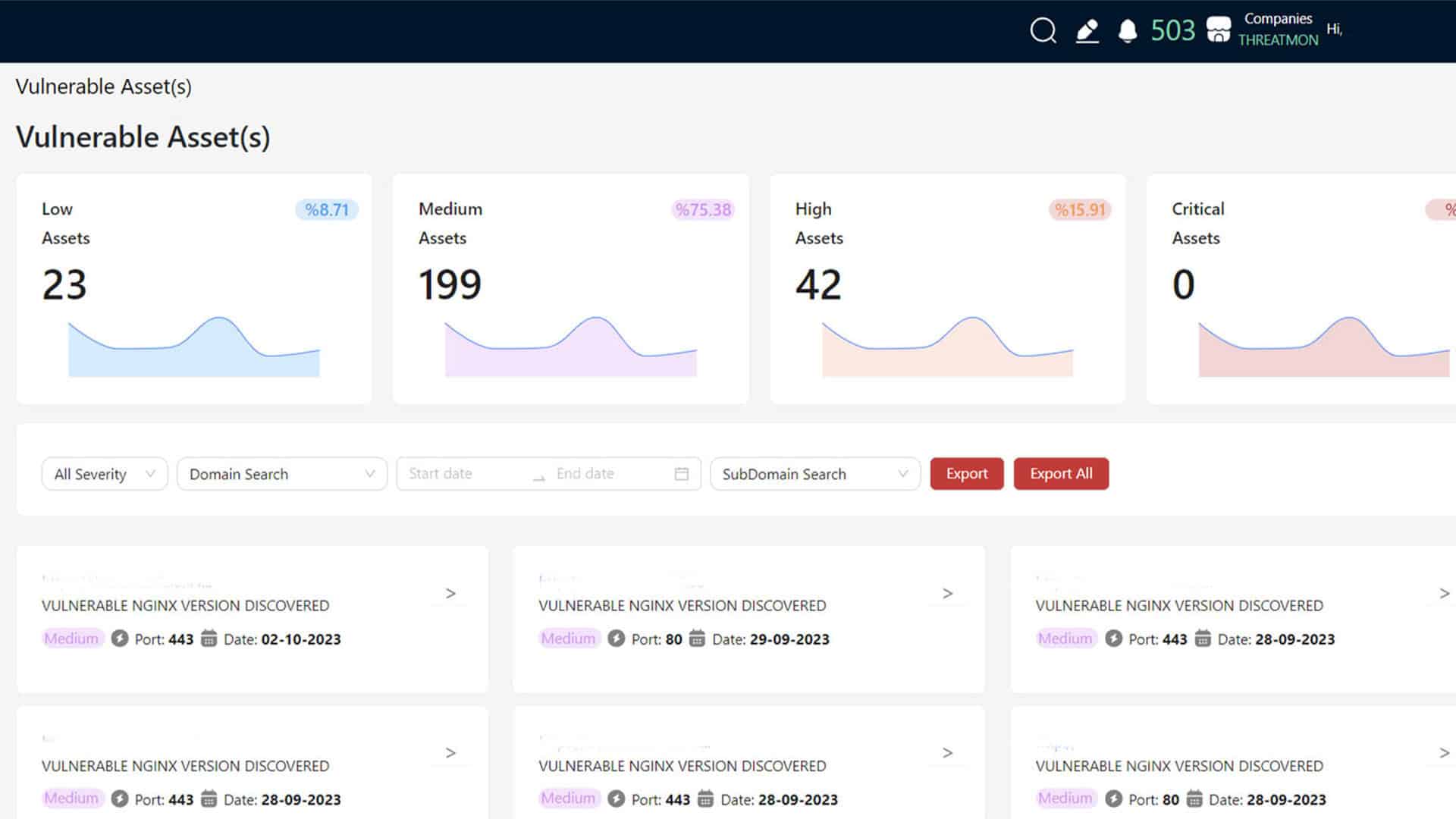
Risk Analysis
Risk analysis with cyber threat intelligence is performed to help organizations understand cyber risks and mitigate their processes as much as possible. In this process, possible cyber attacks against threats that may adversely affect information technology assets should be identified, and risk mitigation recommendations should be made.
Early Detection of Attacks
Cyber threat intelligence helps early detection of ever-evolving threats and mitigates the damage caused by attacks. It is recommended that companies strengthen their cyber defense posture to prevent data breaches that may occur as a result of attacks. When combined with security plans to be created throughout the process, a stronger stance is taken against cyber attacks, and measures are taken against the destructive consequences of breaches.
Protecting Critical Infrastructure
Today, critical infrastructure plays a vital role in the life of societies. As technology continues to advance, attackers are exploiting vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure. We recommend that organizations in these sectors understand the seriousness of cyber attacks and take the necessary precautions. Cyber threat intelligence solutions provide the right protection to society and their services by raising awareness of attacks and prioritizing cyber security measures.
Threat Hunting
Another important point in Threat Intelligence is that there is an active threat-hunting application. The fact that security teams are actively threat hunting to improve the security posture is effective in uncovering zero-day vulnerabilities and APT (Advanced Persistent Threats) or malware of ransomware groups that carry significant risk in cyberspace. 
Phishing Attack Analysis & Response
Phishing monitoring benefits with CTI include protecting your organization against phishing attacks, protecting brand reputation, minimizing financial losses, and maintaining customer trust by proactively addressing phishing threats. 
Clear, Deep, and Dark Web Monitoring
Clear, deep, and dark web monitoring provides information about the organization’s assets, such as stolen credentials or sensitive data. Identifying potential risks arising from the online activities of organizations on the web and analyzing and evaluating the data obtained have valuable results. In addition, various information captured by multiple threat actors is shared publicly or offered for sale in the underground market. The data collected from dark web environments can be associated with a possible attack, and businesses can take preventive measures in this regard.
Security Automation
Advanced cyber threat intelligence solutions utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning applications. In an environment with so much data, processing, analyzing, and integrating the data obtained into machine learning applications strengthens security automation. Thus, it contributes to cyber threat intelligence analysts to focus on the right targets and processes.
Brand Monitoring
CTI carries out studies to detect all kinds of data that may damage the reputation of organizations and to take measures. While protecting their brand reputation, organizations strengthen their cyber stance.
Threat Indicator
Threat indicators are based on models representing objects and behaviors of interest in the cyber security context. By detecting threat indicators, CTI ensures that organizations receive timely updates on the latest threats.
Benefits of Cyber Threat Intelligence for Organizations
Enhancing Security Posture and Defence
CTI enables organizations to identify the most significant risks to their organization by identifying the currently targeted sectors and vulnerabilities being exploited. This strengthens the security posture of organizations by suggesting mitigating measures against risks. An effective cyber threat intelligence study provides a strong defense by collecting and interpreting data and eliminating the false positive rate at the final stage with the review of analysts.
Incident Response and Crisis Management
Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) and Incident Response (IR) strengthen the defense systems of organizations. In a growing and evolving cyber threat environment, different tools need to be used together to manage a potential crisis. For incident response teams, early detection of anomalies and weeding out false positives are of great importance. Threat intelligence uncovers indicators that can be associated with a specific group or type of threat. In this way, it uses information from past attacks, methods, tactics and techniques, and targets to predict and warn of a possible crisis and strengthen the cyber posture.
Contribution to Decision-Making Processes
Another benefit of using Cyber Threat Intelligence is that it supports organizations to produce faster and more effective results in decision-making processes in the event of a possible threat. Threat intelligence includes threat actor profiling and understanding their goals, strategies, motivations, and vulnerabilities. When this comprehensive data is brought together, organizations will produce output close to clarity in their decision-making processes as a result of deep analysis and inferences. ThreatMon cyber threat intelligence teams can support your organization to take proactive measures against threats with its experienced staff.
Threat Intelligence Lifecycle
Planning
The Planning cycle determines the planning and roadmap for the collection process based on the requirements for threat intelligence. At this stage, security teams start working on what kind of intelligence to collect, what to do to improve the defense against attack, and what to achieve results according to the project’s purpose. Data collection For threat intelligence, this is the step in the reconnaissance process where we start collecting sources and data. Sources where information needs to be collected: Data is collected from sources such as blogs, forums, communities, etc. 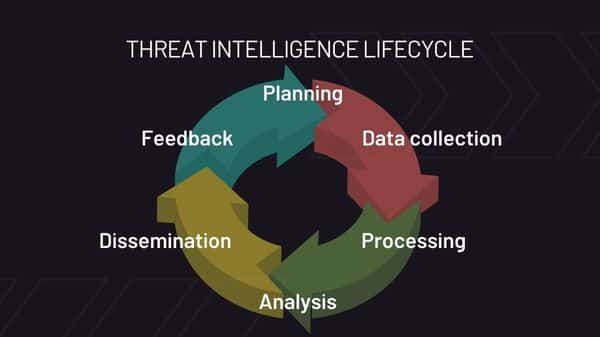
Processing
Before the Threat Intelligence team processes the collected information, work is done to check and structure the data. The process of associating and classifying the data takes place during this cycle.
Analysis
It is the process of transforming processed information into intelligence. After this stage, it is the process of taking steps to prevent attacks in case of a threat, strengthening security controls, and providing additional security configurations where necessary.
Dissemination
Prepares the completed intelligence data into a concise, concise report by format without adhering to technical jargon and delivers it to the relevant departments.
Feedback
This is the stage where the actionability and accuracy of the intelligence delivered to the relevant units are evaluated, and the organization returns to the relevant issue. The threat intelligence lifecycle is a construct that organizations perform continuously. Organizations use these steps to create and develop intelligence in an iterative cycle, using different methods and techniques.
Implementation Strategy of Cyber Threat Intelligence
The cyber threat intelligence implementation strategy should be such that it best meets the needs of businesses. Cyber threat intelligence is shared with relevant institutions and individuals after providing an actionable prediction for the future, and the necessary technologies, detailed analysis, and evaluations are provided to prevent possible cyber risks.
Creating a Plan
Good planning is the first essential component of a robust cyber threat intelligence program. When starting cyber threat intelligence, it is necessary to know who needs intelligence, who to include in the intellect, and identify new threat patterns. Providing a meaningful context for the business and the security team is essential.
Collecting Cyber Threat Intelligence
Resources, tools, and methods are identified to gather cyber threat intelligence. Intelligence data is collected from various sources using predetermined Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures. Cyber threat intelligence sources can be public data sources, relevant forums, social media, and traffic logs.
Managing Vulnerabilities
Vulnerability management is one of the issues that should not be ignored. Hundreds of problems are detected every day with vulnerability management. Identifying and remediating vulnerabilities is an important component of the cyber threat intelligence process.
Evaluation and Analysis
The collected data should be analyzed and put into a usable form. The reliability of the data obtained and the suitability of the source are evaluated. With the data obtained during the analysis phase, the possibility of a possible attack can be detected, or inferences can be made by providing insight through attack models.
Transmission
After completing this process, the information obtained is forwarded to the necessary places. As a result of many processes and features, such as the competence of the threat intelligence team, the amount and variety of data sources collected, and the fulfillment of the planned program, a properly implemented cyber threat intelligence program achieves its ultimate goal.
Collection and Analysis of Cyber Threat Intelligence
Data Sources and Collection Methods
Threat intelligence includes data collected from many different sources. We can analyze these data sources under three headings;
- Internal Sources: Internal sources are usually logs, network traffic, and scan data.
- Technical Sources: Technical sources are databases where vulnerabilities are shared, data such as threat flows.
- Human Sources: Intelligence data is collected through human scanning and research. Human sources are data obtained from the dark web, hacker forums, ransomware blogs, black markets, and chat rooms.
Data Analysis and Evaluation
Obtaining threat intelligence data from so many different sources brings with it complexity. In this complex data space, it is necessary to process what is truly important and valuable and to separate the processed data from the false positives to arrive at an accurate output. The assessments and insights of threat intelligence analysts are necessary here. The collected data should be evaluated, and essential and valuable information should be made available to the relevant institutions. Our cyber threat intelligence platform, ThreatMon, aims to increase your resilience in cyberspace by analyzing the most critical threats for you with its experience and expert team.
Cyber Threat Intelligence and Privacy Ethics
Data Privacy Concerns in Cyber Threat Intelligence
With the development of technology, the threat environment is changing rapidly. With these developments, privacy issues come to the fore if necessary precautions are not taken. This is a serious agenda that all businesses and individuals, large and small, should not take lightly. The impact of assets in the risk category as a result of possible data breaches can cost organizations much more.
Ethical Rules and Standards
Preventing cyber threats requires a balance between protecting the privacy and freedoms of society. To address these ethical issues, cybersecurity professionals need to emphasize ethical principles such as transparency and debriefing. This will help to increase public trust in cybersecurity practices.
The Future of Cyber Threat Intelligence
Emerging Threats and Trends
It is an undeniable fact that cyber threats have increased rapidly compared to previous years. This increase in threats also brings with it a financial increase. The increase in threats shows that threat actors have higher financial expectations, given the value of organizations’ data. In support of this claim the examples of data below will reveal to us that: In 2021, the FBI reported that ransomware attacks were the most common type of cybercrime reported to the agency. Ransomware attacks are motivated by financial gain, as hackers demand payment from victims to decrypt their data. In 2022, the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report found that financial gain was the primary motivation in 82% of all data breaches. In 2023, the Microsoft Digital Defence Report found that financial gain was the primary motivation in 73% of all cyberattacks reported to Microsoft. Furthermore, if we deep dive into the IC3 report of 2021, with a total of 2,760,044 complaints, $18.7 billion- $49.2 billion of which was caused by ransomware was reported.
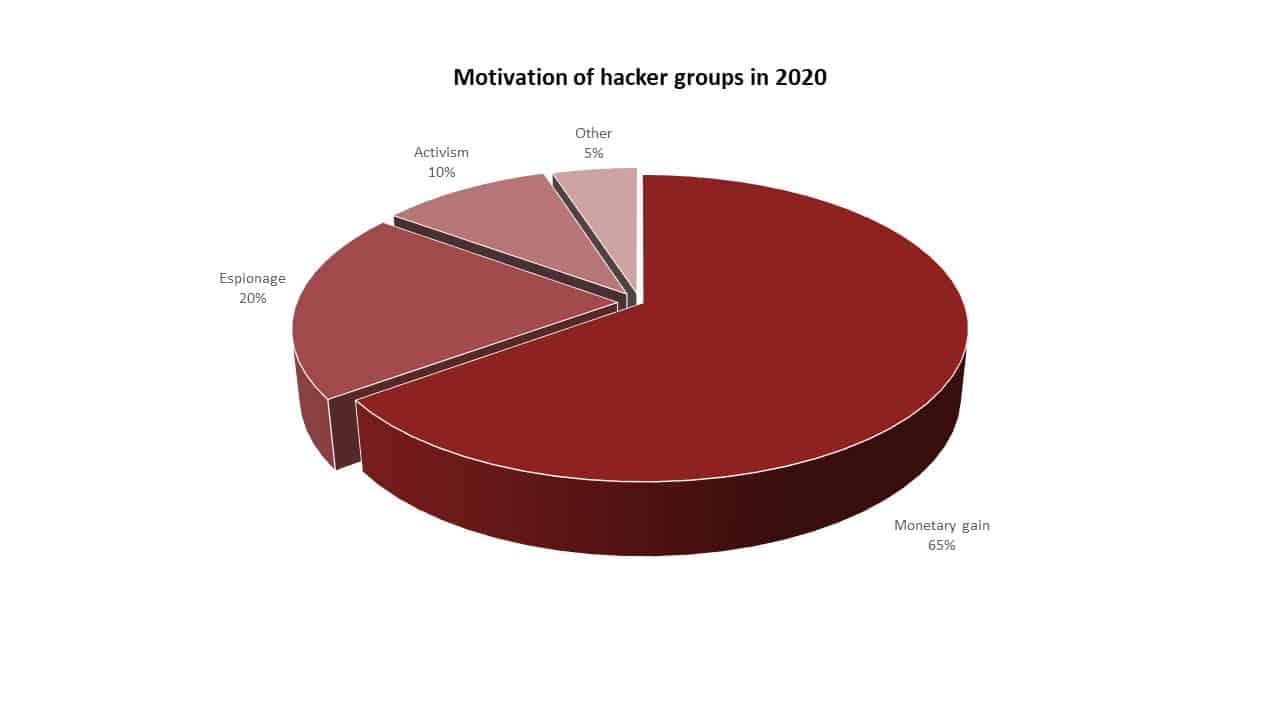
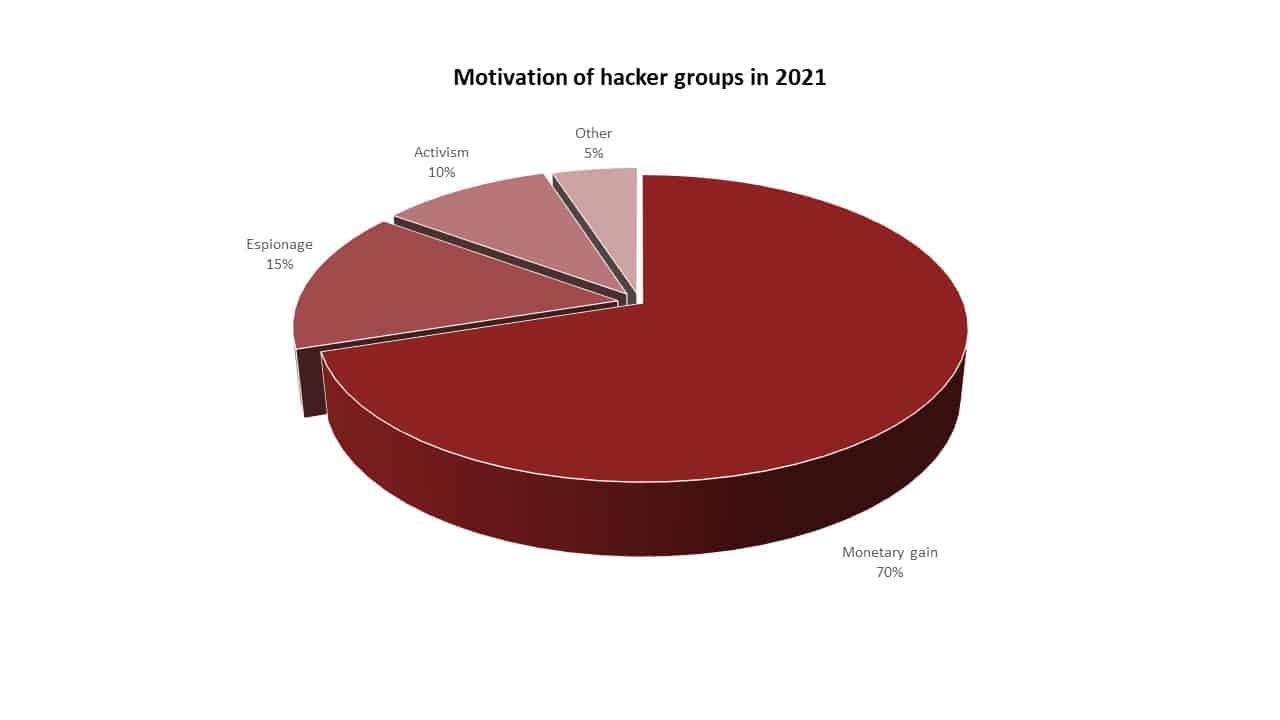
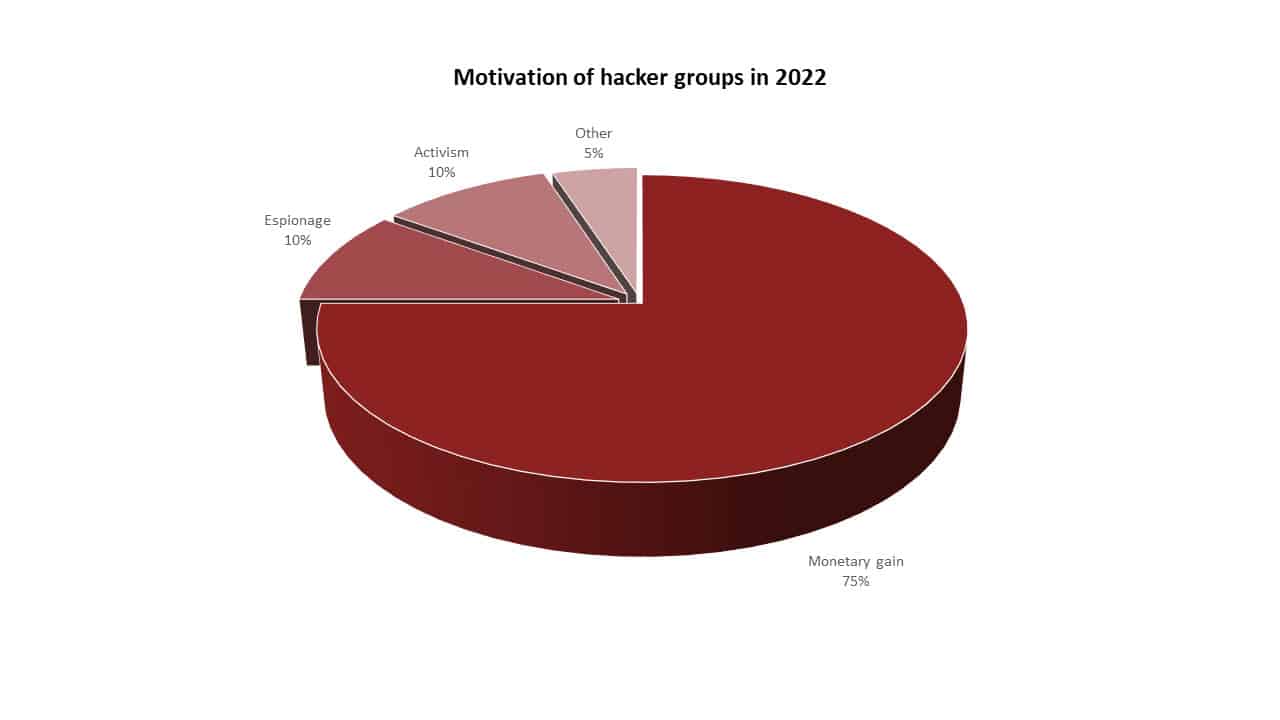
Increasing technological advances and trends, the development of artificial intelligence, machine learning, automation, and predictive analytics, and the increasing usage of IoT devices will lead to new attacks and possibly different opportunities for businesses. It is obvious that a system with many components, such as software, is more likely to have more vulnerabilities as the number of components grows, and it will be harder to track the point of attack. Besides that, as we can see from the Verizon Data Breach Investigation Report in 2022, Email attacks, with 82% of all data breaches, were the foremost exploited attack surface for hackers, with phishing attacks being the most common type of email-based attacks. By the same reasoning, a system with a large number of users will also reveal more attack surfaces to the attackers. When the threats awaiting organizations in the future of cyber threat intelligence are analyzed:
- Ransomware attacks pose a major threat. Our Experts at ThreatMon recommend that organizations take precautions against ransomware threats by leveraging threat intelligence to conduct sectoral and geographic target analysis and close security gaps.
- Almost most cybercrimes are committed by collaborative groups. As the size and complexity of the attack increase, the attacker is not a single person but a group of people with different specializations.
- The use of botnets and automated malware distribution tools is increasing day by day. With the development of artificial intelligence, it is seen that malware tools are creating tools integrated with this technological development. This increase targets critical infrastructures, large enterprises, and small businesses.
- Scenarios in which nation-states are backed by groups of threat actors are on the rise, and as a result, the tendency for more sophisticated attacks to emerge is increasing. The combination of increasing sophistication of threat actors and nation-state support is likely to expose organizations to serious threats.
- And of course, the human factor is the most dangerous because credentials, personal information, and even remote connections to employees’ computers are sold over the Internet. On top of that, with the increasing use of technology, people have become more accessible.
Advancements in Cyber Threat Intelligence Technologies
It is important to integrate technological developments into cyber threat intelligence. As analysts, when we look at the issues that are important in today’s world, we see that artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing stand out. Cyber threat intelligence platforms can produce more effective results by integrating this developing technology into their structures. Since cyber threat intelligence uses complex and massive amounts of data, combining and supporting this data with artificial intelligence is important. In addition, by including cloud computing in cyber threat intelligence processes, the risks and vulnerabilities that may occur in this technology should be identified and organizations should be provided with the guidance they will need.
How To Select a Threat Intelligence Platform
With so many threats, vulnerabilities, and risks, you understand the importance of threat intelligence. So, when it comes to choosing a threat intelligence platform, how should you choose?
Diversity and Reliability of Data
The first important feature of threat intelligence is the diversity and reliability of data sources. For this, it is important to obtain sensitive data about your organization, threats covering your sector, geographical region, and assets from various sources such as the dark web, clear web, external sources, open source, social media, and active endpoints.
Integration and Automation with Other Security Tools
The threat intelligence platform should provide integration with other tools used for organizations. When choosing a platform, it is important that it can integrate with different tools such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), Endpoint Security Solutions, and Firewalls. In addition, cyber threat intelligence should have Advanced Automation capabilities that can detect security issues with a minimum false/positive rate.
Reports and Support
The cyber threat intelligence platform should evaluate the risks and targets of existing threat actors according to organizations, provide information, and support them with reports. In addition, another important point for organizations is to receive service and support from the platform in case of a possible problem.
Actionable Cyber Threat Intelligence with ThreatMon
What is ThreatMon?
ThreatMon uses a combination of cyber intelligence and attack surface discovery to deliver early warning and contextual insights on external cyber threats. The platform uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to provide a comprehensive view of the external cyber environment, giving organizations a better understanding of potential risks and helping them prepare for impending attacks. ThreatMon is a cloud-based solution that can be accessed from anywhere. The modules within the platform provide state-of-the-art and comprehensive solutions.
How does ThreatMon help with Cyber Threat Intelligence?
ThreatMon is a platform that provides cyber threat intelligence, attack surface management, and digital risk protection solutions through comprehensive data analysis and the latest generation technology development. ThreatMon’s Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) solution strengthens your defenses by understanding the cybercrime actors targeting your organization, their motivations, and behaviors. With continuous monitoring capabilities, this module provides real-time updates on emerging threats, enabling proactive defense and timely response. It also offers customizable threat intelligence feeds that can be tailored to the specific needs of organizations. ThreatMon’s Attack Surface Management helps you identify your organization’s external digital assets and continuously monitor them for security threats. You can receive push notifications when a new vulnerability is discovered in your assets and detect advanced anomalies in your digital assets. ThreatMon’s Digital Risk Protection solution helps identify emerging threats and threat actors. This enables organizations to be better prepared for attacks and take the necessary precautions. Through continuous threat analysis and monitoring, organizations can better understand the cyber threat landscape and mitigate their risks by taking appropriate measures. ThreatMon Cyber Threat Intelligence Platform enables rapid intervention and prevention of potential damage in case any vulnerability or malicious activity is detected.
What are the most significant features of ThreatMon for CTI?
ThreatMon offers businesses a comprehensive cybersecurity solution to protect their digital assets from external threats. The platform makes cyber defense more comprehensive by combining Threat Intelligence, Attack Surface Management, and Digital Risk Protection in a state-of-the-art product with AI and machine learning at the forefront. ThreatMon’s big data processing technology detects potential long-term threats and provides preventive measures to protect companies from future attacks. Our platform offers customized solutions by assessing the specific needs of each business. ThreatMon provides organizations with a proactive and robust defense against advanced cyber-attacks by revealing previously unknown threats with different and specially developed modules. Join organizations leveraging ThreatMon’s advanced expertise to protect their digital assets and have a comprehensive defense in cyberspace.
A cyber threat is a malicious act that aims to damage, steal, modify, or corrupt data. Examples of cyber threats include ransomware, viruses, DDOS attacks, and other malicious actions.
One of the most important things when collecting threat intelligence data is to collect data from as many different sources as possible. These sources can be tools that provide log records used within the organization, honeypots, communication channels, hacker forums, dark web, and sources that provide IOC. By using many different sources, the sources of false positives are identified, and the minimum false positive rate is ensured. The data obtained is evaluated and processed by expert analysts. Advanced threat intelligence platforms utilize machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies to increase the value of data.
Cyber threat intelligence involves the process of collecting data from various sources, identifying and working on the information, improving the data, and using it by decision-makers. This process is the cyber threat intelligence life cycle. This process starts with the planning of the intelligence and continues until the return process.
Although the intelligence cycle consists of 6 stages, the process is cyclical and repetitive.
Cyber threat intelligence constitutes a preventive measure against cyber attacks. In today’s world, where cyber-attacks are increasing day by day, threat intelligence aims to prevent attackers from entering the exploitation phase. With technical, tactical, and procedural analysis, it is ensured that possible attacks are prevented based on past attacks. By analysing and processing useful data in the large data pool provided by cyber threat intelligence, an attack can be prevented by making contextual inferences, and businesses can take countermeasures.
Threat intelligence involves collecting, analysing and evaluating information about your business. The cyber threat intelligence framework supports the processes of planning, maintaining and improving your threat intelligence activities. organisations can develop the threat intelligence framework according to their needs.
A cyber threat intelligence analyst is someone who monitors attack risks, analyzes malware, transforms raw information into valuable data and finalises intelligence data. A cyber threat intelligence analyst evaluates data obtained through AI applications separates false positives from threats, highlights threats with the highest risk, and provides mitigation and guidance to businesses. It also provides the reports and support they need according to the request of the organizations.
Cyber threat intelligence provides comprehensive asset analysis and assessment of an organization. Threat intelligence is information that analyzes the organization’s attack risks, identifies the potential risks of being targeted by an attacker, and provides preventive measures to take proactive measures.
Threat hunting is the practice of identifying unrecognized threats on the network or in data. With threat hunting, potential malicious threat actors can be investigated in depth to identify their techniques and possible targets.
Attack surface analysis enables organizations to know their inventory and identify the assets they need to defend. Attack surface detection identifies potential vulnerability points that an attacker can target. Attack surface analysis reveals vulnerabilities where an attacker can gain unauthorized access to the enterprise’s system, network or application. Thus, organizations can prevent a possible attack by closing their vulnerabilities.
Cyber threats can come from a wide variety of sources, such as individual hackers, hacker groups, former corporate employees, hostile nation-states, terrorist groups, or state-sponsored APT groups.
Cyber threat intelligence supports and benefits organizations in many different ways. For example
- Automates threat data collection.
- Integrates tools, teams, and workflows.
- It helps you stay updated with the latest threats and shows potential threats.
- Aim to mitigate threats before they harm you.
- Analyzes the techniques and goals of threat actors with static and dynamic malware analysis.
- Vulnerability intelligence identifies risks and provides mitigations.
By monitoring threat actors’ TTPs (Tactics, Techniques and Procedures), organisations can see potential targeted attacks and strengthen their security posture.







