
External Attack Surface Management (EASM) is vital to modern cybersecurity strategies. EASM is gaining importance as organizations’ digital footprints expand and they are exposed to new vulnerabilities. In this content, crafted by the experts at ThreatMon, we will delve into External Attack Surface Management and its importance for businesses seeking to fortify their defenses against external threats. Companies must recognize that traditional security measures such as firewalls, antivirus software, and reactive incident response are insufficient in isolation. Through discovery, assessment, and continuous monitoring of external digital assets, EASM enables organizations to preemptively identify and mitigate vulnerabilities, safeguarding against financial losses and reputational harm that could arise from security breaches. Implementing a robust EASM solution that utilizes advanced technology offers a proactive approach to managing and reducing the risks associated with external cyber threats.
The external attack surface of an organization refers to all the digital and physical assets, services, and entry points that are exposed to the Internet or external entities, making them accessible—and potentially vulnerable—to external attackers. This includes any component of the organization’s technology infrastructure that can be discovered and potentially exploited from outside the organization’s internal network. Managing and securing this external attack surface is crucial for protecting an organization from cyber threats, data breaches, and unauthorized access.
The external attack surface of an organization encompasses a wide array of digital and physical assets accessible to external entities, making them potential targets for cyber attackers. This includes publicly accessible websites and web applications that serve as the digital face of the organization, as well as exposed network services such as email, DNS, and FTP servers, which are critical for daily operations but vulnerable if not properly secured. Cloud services, including storage, web applications, and databases, are also a part of this surface, especially when configured to be accessible over the Internet. Remote access points like VPNs and remote desktop services extend the workplace beyond its physical boundaries and expand the attack surface. Internet-facing devices, including IoT devices and security cameras, further contribute to the exposure, as do publicly available APIs that allow external interactions with the organization’s systems.
Additionally, an organization’s presence on social media and other digital platforms, through official accounts and profiles, represents another aspect of the external attack surface, offering information and interaction points that could be exploited maliciously.
These components constitute the external attack surface, through which unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security incidents can occur if not adequately managed and secured.
External Attack Surface Management (EASM) is a cybersecurity discipline focused on identifying, assessing, and managing an organization’s external digital assets visible on the Internet or accessed remotely. These assets include websites, web applications, servers, cloud services, and internet-connected devices. The main goal of EASM is to reduce the risk of cyber attacks by minimizing the exposure of vulnerabilities and ensuring that only authorized assets are accessible from the outside.
Organizations increasingly rely on digital technologies, which expand their external attack surface and provide opportunities for cyber attackers to exploit vulnerabilities. EASM helps organizations to proactively manage these risks by providing visibility into their external digital footprint, enabling them to detect and respond to vulnerabilities and threats before they are exploited.
Effective EASM requires continuous effort and integration with an organization’s cybersecurity strategy. It involves collaboration across teams, including IT, security, and business units, to ensure comprehensive coverage and alignment with business objectives.
External Attack Surface Management (EASM) is pivotal in enhancing an organization’s security posture by identifying, assessing, and securing external digital assets. Different teams within an organization can benefit from EASM in unique and impactful ways.
Improved Visibility: EASM provides these teams with a comprehensive view of all external-facing digital assets, including cloud services, web applications, and APIs. This enhanced visibility enables better management and security of these assets.
Efficient Network Management: By identifying vulnerabilities and potential entry points from the outside, IT and network teams can implement more effective network segmentation and firewall rules, improving overall network security.
Proactive Threat Detection: EASM aids in the early detection of external threats and vulnerabilities, allowing security teams to shift from a reactive to a proactive security approach. This early detection is critical for preventing potential breaches.
Streamlined Incident Response: By clearly understanding the external attack surface, these teams can respond more effectively to incidents, reducing the time and resources required to mitigate threats.
Regulatory Compliance Assurance: EASM helps ensure external digital assets comply with relevant data protection and cybersecurity regulations. This is vital for avoiding penalties and legal issues associated with non-compliance.
Risk Assessment and Reporting: These teams can use data from EASM to conduct detailed risk assessments and generate reports that inform decision-making and strategy at the highest levels of the organization.
Secure Development Lifecycle: EASM integrates security into the development lifecycle by identifying vulnerabilities in externally facing applications before deployment. This enables development teams to address security issues early, creating more secure products.
Enhanced Product Security: Product teams benefit from EASM by gaining insights into potential security weaknesses in their products, allowing for timely updates and patches to protect against external threats.
Informed Decision-Making: Executives receive actionable intelligence from EASM efforts, helping them make informed decisions regarding cybersecurity investments, policies, and strategies.
Reputation and Trust: By demonstrating a commitment to securing the external attack surface, leadership can protect the organization’s reputation and maintain trust among customers, partners, and stakeholders.
Brand Protection: EASM contributes to brand protection by preventing breaches that could lead to negative publicity. Keeping customer data safe enhances brand trust and loyalty.
Customer Confidence: By ensuring the security of customer-facing applications and services, these teams can reassure customers that their data is protected, enhancing customer confidence and satisfaction.
Data Breach Mitigation: In the event of a security incident, EASM provides critical information that can help these teams manage legal risks and public relations challenges more effectively, minimizing potential damage to the organization.
EASM’s targeted focus on external assets offers significant benefits across an organization. It helps to protect against external threats, ensure compliance, safeguard the brand, and ultimately support the organization’s strategic objectives.
The process of identifying all an organization’s external-facing digital assets, including websites, web applications, APIs, cloud services, and internet-connected devices.
The evaluation of external digital assets to identify security weaknesses, misconfigurations, and vulnerabilities that cyber attackers could exploit.
Information and analysis concerning current or emerging threats and vulnerabilities that can inform an organization’s cybersecurity strategies and defenses. Click here to learn more about Threat Intelligence.
The process of assessing the identified vulnerabilities to determine their potential impact on the organization and prioritize them based on their risk level.
Actions to address vulnerabilities identified during the assessment phase. Remediation involves directly fixing the vulnerability, while mitigation refers to steps taken to reduce the impact or likelihood of a vulnerability being exploited without necessarily fixing it.
The ongoing surveillance of an organization’s external attack surface to detect new assets, vulnerabilities, and suspicious activities that could indicate a threat.
The set of procedures an organization follows in response to a detected cybersecurity incident to manage and mitigate its impact.
Ensuring the organization’s external digital assets adhere to relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards related to cybersecurity and data protection.
The process of managing updates for software and systems, including the identification, acquisition, installation, and verification of patches for vulnerabilities in external assets.
This security concept centers on the belief that organizations should not automatically trust anything inside or outside their perimeters and must verify everything trying to connect to their systems before granting access.
The method of converting data into a code to prevent unauthorized access, particularly important for protecting data transmitted across or stored on external assets.
Measures taken to protect application programming interfaces (APIs) from being exploited by cyber attackers, including authentication, authorization, and encryption techniques.
The process of identifying and addressing cybersecurity risks and misconfigurations in cloud environments. It is an essential part of managing the external attack surface for organizations using cloud services.
The collective presence of an organization’s external digital assets on the Internet, including all information traced back to the organization through web services, social media, and other online platforms.
Measures aimed at protecting DNS infrastructure from cyber threats, ensuring the proper resolution of domain names without interception or manipulation.
A network security device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules, acting as a barrier between secure internal networks and untrusted external networks.
Protocols for establishing authenticated and encrypted links between networked computers, crucial for securing data in transit over the Internet.
A specific application firewall that filters, monitors, and blocks HTTP traffic to and from a web service, protecting web applications from various attacks.
An authorized simulated cyber attack on a computer system performed to evaluate its security. It is a critical component of EASM for identifying vulnerabilities in external assets.
The process of identifying, understanding, and addressing threats and potential vulnerabilities in an application or system used to improve security posture.
A type of cyber attack in which stolen account credentials, typically obtained from data breaches, are used to gain unauthorized access to user accounts through large-scale automated login requests.
An attack surface encompasses various dimensions through which an organization can be vulnerable to cyber threats. Understanding these types helps in formulating targeted defense strategies.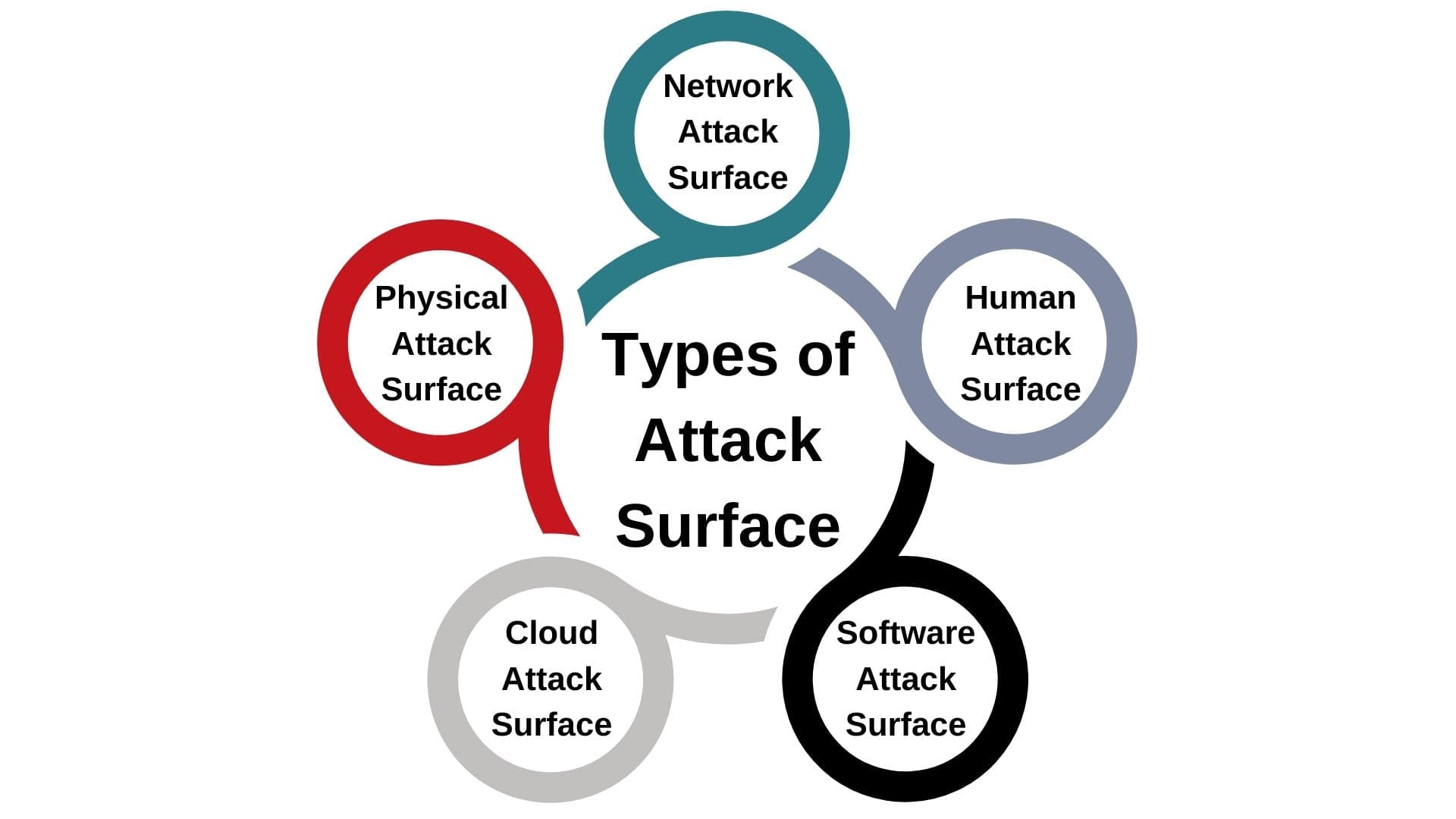
This type refers to all the physical means through which an unauthorized individual could access a company’s devices or premises to launch an attack. It includes direct access to servers, workstations, laptops, and networking devices. Physical security breaches can occur through stolen devices, USB drives used as a vector for malware, or unauthorized access to secure locations housing critical infrastructure.
The digital attack surface comprises all the software, networks, and technology assets that interact with or are accessible via the Internet. This includes websites, email servers, cloud services, and open ports on the network. This surface contains vulnerabilities within software applications, misconfigurations in databases, and unpatched systems. As organizations increasingly move data and operations online, the digital attack surface expands, opening more avenues for potential cyber attacks.
The human attack surface focuses on the potential for security breaches initiated through social engineering attacks on an organization’s employees or other affiliated individuals. Phishing, spear-phishing, pretexting, and other forms of manipulation deceive individuals into granting access to sensitive information or secure systems. This surface highlights the importance of security awareness and training as a critical defense mechanism.
Specifically, it refers to software application vulnerabilities, including internal applications and third-party services. It’s often considered a subset of the digital attack surface but is sometimes highlighted separately due to software’s critical role in an organization’s operations.
With the adoption of cloud computing, the cloud attack surface has become a significant concern. It includes data stored in cloud services, cloud-based applications, and the configuration of cloud resources. Misconfigurations and inadequate access controls in the cloud can lead to data breaches and unauthorized access.
Each type of attack surface requires specific strategies and tools for effective management and protection. For instance, securing the physical attack surface might involve access controls and surveillance, whereas protecting the digital attack surface could require firewalls, encryption, and vulnerability management programs. Similarly, mitigating risks associated with the human attack surface often relies on continuous education and phishing simulation exercises to enhance awareness among employees and stakeholders. Understanding and addressing these diverse attack surfaces is the cornerstone of any organization’s robust cybersecurity posture.
External Attack Surface Management (EASM) is fundamentally designed to help organizations keep pace with the rapid expansion of their digital footprints due to ongoing digital transformation, the adoption of cloud services, and the integration of internet-connected devices. This expansion has resulted in broader and more complex attack surfaces, increasing the opportunities for cyber attackers to exploit vulnerabilities. EASM addresses these challenges through a multifaceted approach.
EASM enhances visibility across the organization’s external digital assets. It employs advanced discovery tools to identify and catalog web applications, APIs, cloud resources, and internet-connected devices, including those previously unknown or unmanaged. This comprehensive visibility is crucial for understanding the full scope of the external attack surface and ensuring that no asset remains overlooked and vulnerable to attack.
EASM involves continuous and automated scanning for vulnerabilities within these external assets. As digital footprints expand, so too does the potential for vulnerabilities. Identifying these vulnerabilities early allows organizations to prioritize and remediate them effectively, reducing the risk of exploitation. EASM tools assess and prioritize vulnerabilities based on potential impact and exploitability, enabling organizations to allocate their remediation efforts where they are most needed.
Another key aspect of EASM is its contribution to a proactive security posture through continuously monitoring suspicious activities and emerging threats. This capability is increasingly important as the attack surface expands, introducing new vectors for potential attacks. Continuous monitoring enables organizations to detect and respond to threats more swiftly, minimizing the potential for damage.
As organizations expand digitally, maintaining compliance with cybersecurity regulations and standards becomes more complex. EASM assists in this area by keeping an up-to-date inventory of external assets and vulnerabilities, supporting compliance efforts, and providing documentation of risk management practices.
EASM supports organizations in their digital transformation and cloud adoption initiatives. It offers specialized tools and practices for managing cloud-based assets and services, ensuring these environments are securely configured and monitored. This includes identifying misconfigurations in cloud storage, monitoring cloud-based applications for vulnerabilities, and safeguarding cloud environments against potential security breaches.
External Attack Surface Management is a critical strategy for modern organizations facing the challenges of an expanding digital presence. By enhancing visibility, facilitating timely vulnerability management, supporting proactive threat detection, ensuring compliance, and adapting to digital and cloud initiatives, EASM enables organizations to navigate the complexities of today’s cybersecurity landscape effectively.
External Attack Surface Management (EASM) solutions bolster cybersecurity postures across diverse scenarios. Their applications span from preemptive threat identification to compliance enforcement, offering organizations a comprehensive toolkit to address external security challenges.
Comprehensive Asset Discovery
Organizations often struggle to maintain an up-to-date inventory of their digital assets, especially as they expand and evolve. EASM solutions automate the discovery process, identifying all external-facing assets, including those that may have been overlooked, forgotten, or unauthorized. This complete visibility is the first step in securing the external attack surface.
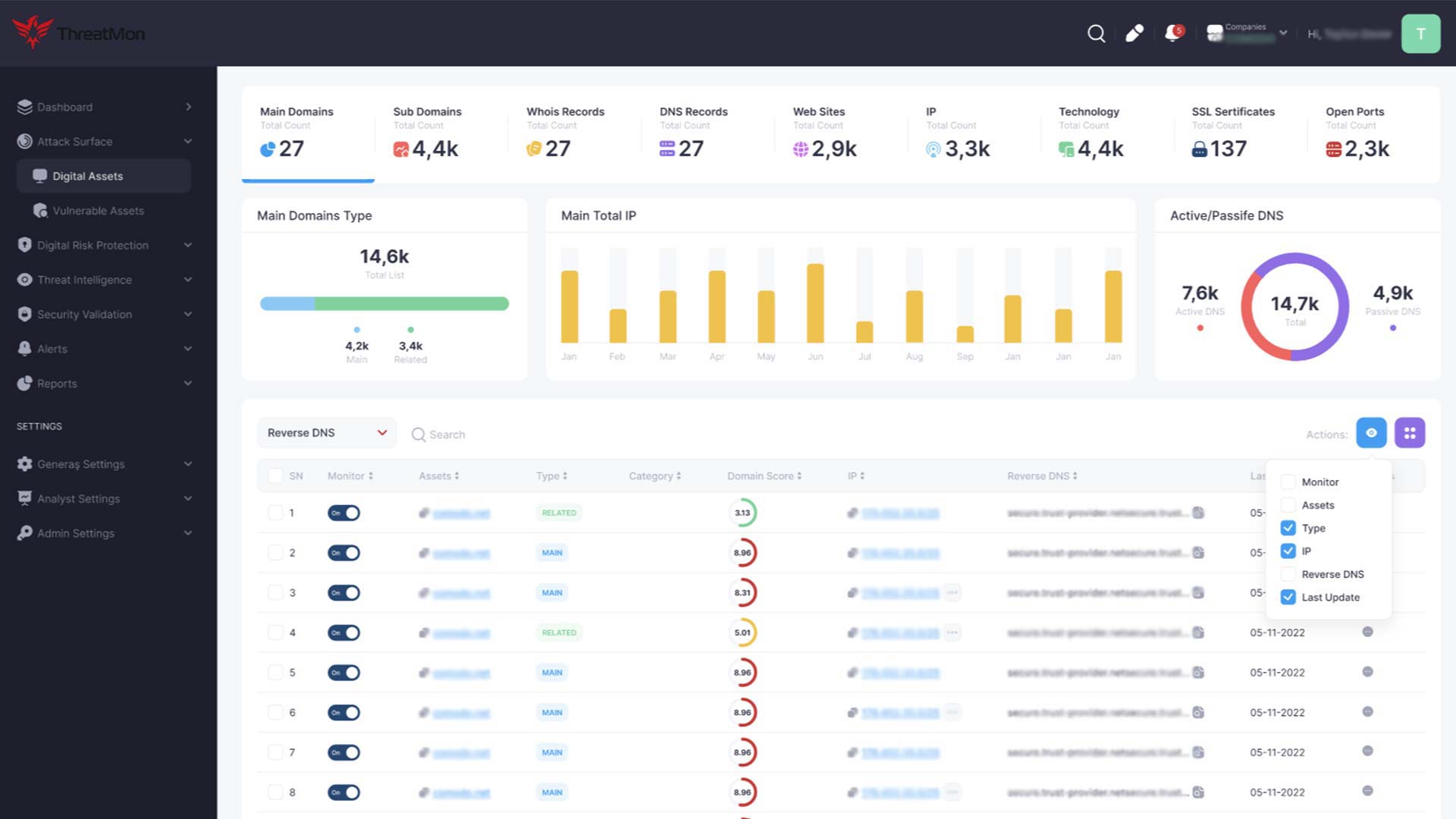
EASM solutions scan identified assets for vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and other security weaknesses. By leveraging advanced algorithms and threat intelligence, these solutions can prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity and the potential impact on the organization. This prioritization lets security teams focus on remediating the most critical issues first.
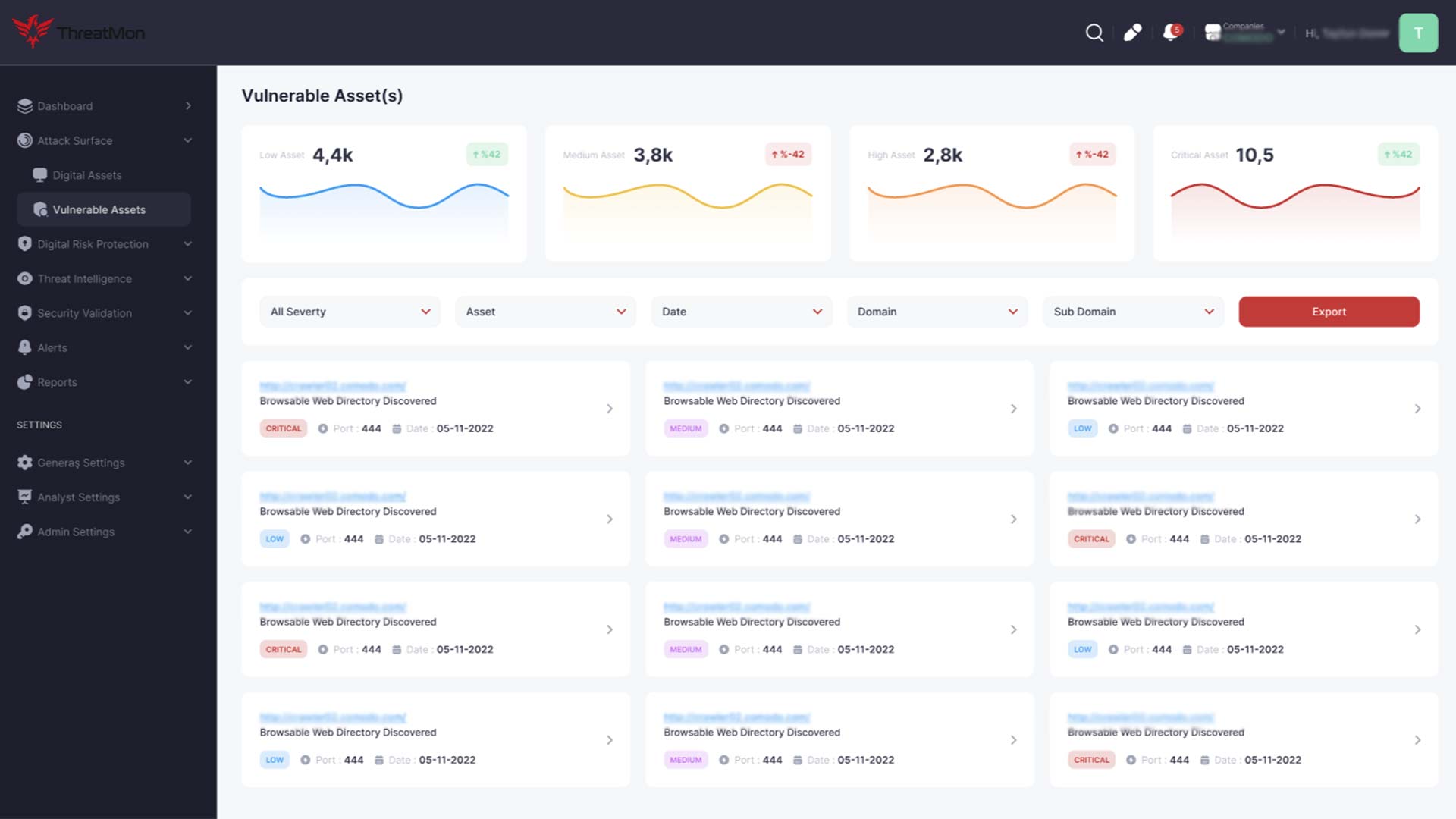
EASM solutions help organizations secure their cloud-based assets with the increasing adoption of cloud services. They identify misconfigurations, excessive permissions, and compliance violations in cloud environments, enabling teams to address these issues promptly and prevent potential breaches.
Organizations rely on various third-party vendors and partners, each with its own set of external digital assets that could introduce risks. EASM solutions help assess and monitor these third parties’ security postures, ensuring their vulnerabilities do not compromise the organization’s security.
Many industries are subject to strict regulatory requirements regarding data protection and cybersecurity. EASM solutions assist organizations in maintaining compliance by ensuring that all external-facing assets adhere to relevant standards and regulations, thereby avoiding potential fines and penalties.
EASM solutions can aid incident response teams in a security incident by providing detailed information about the attack vectors and affected assets. Additionally, by continuously monitoring for suspicious activities, EASM solutions enable proactive threat hunting, helping to identify and neutralize threats before they result in a breach.
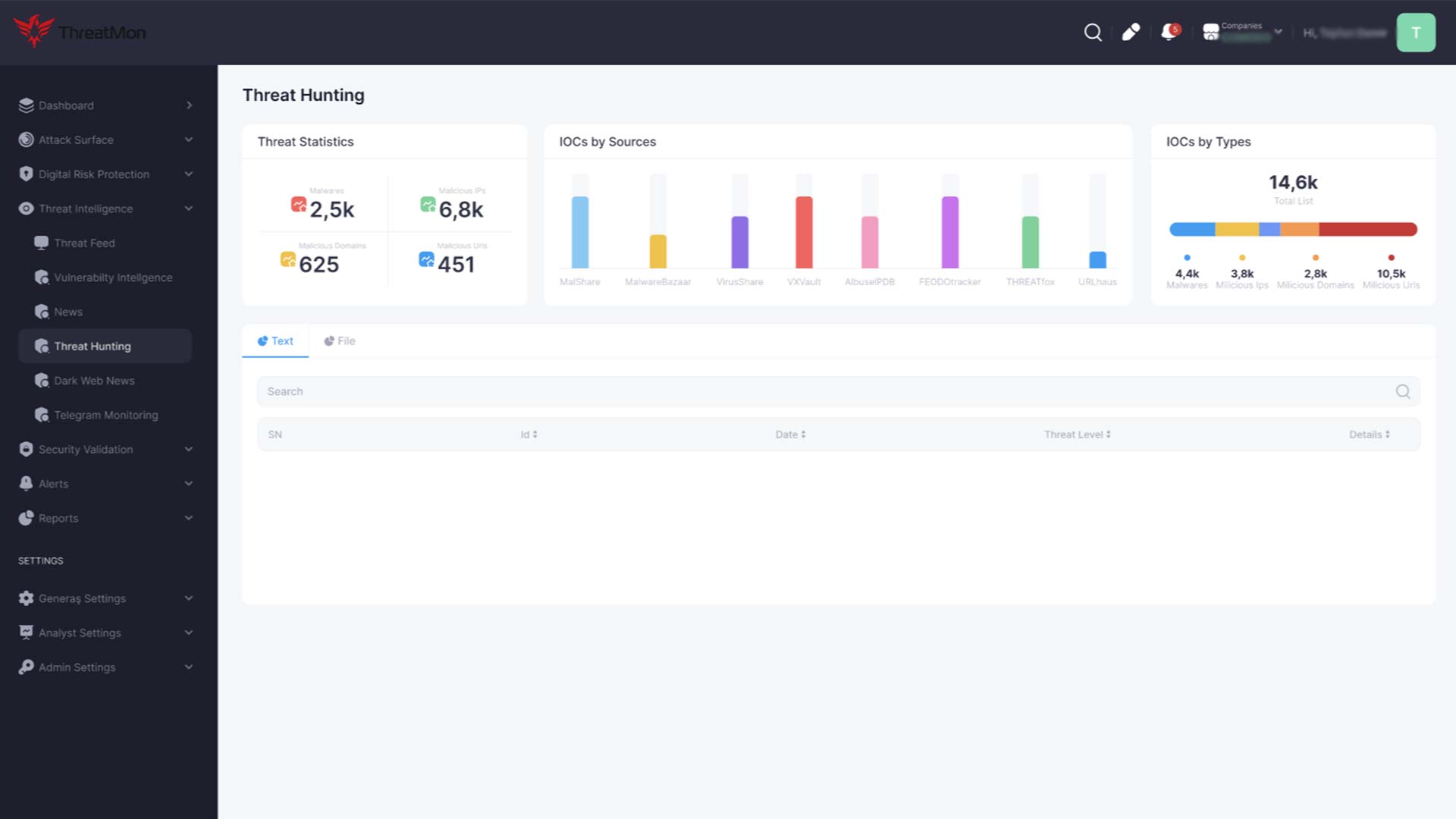
EASM solutions can detect brand impersonation, counterfeit websites, and phishing campaigns targeting organizations or customers. By promptly identifying and addressing these fraudulent activities, organizations can protect their brand reputation and prevent potential financial losses.
These use cases illustrate the versatility and value of External Attack Surface Management solutions in addressing a wide range of cybersecurity challenges. By implementing EASM, organizations can enhance security posture, mitigate risks, and maintain compliance in an increasingly complex digital landscape.
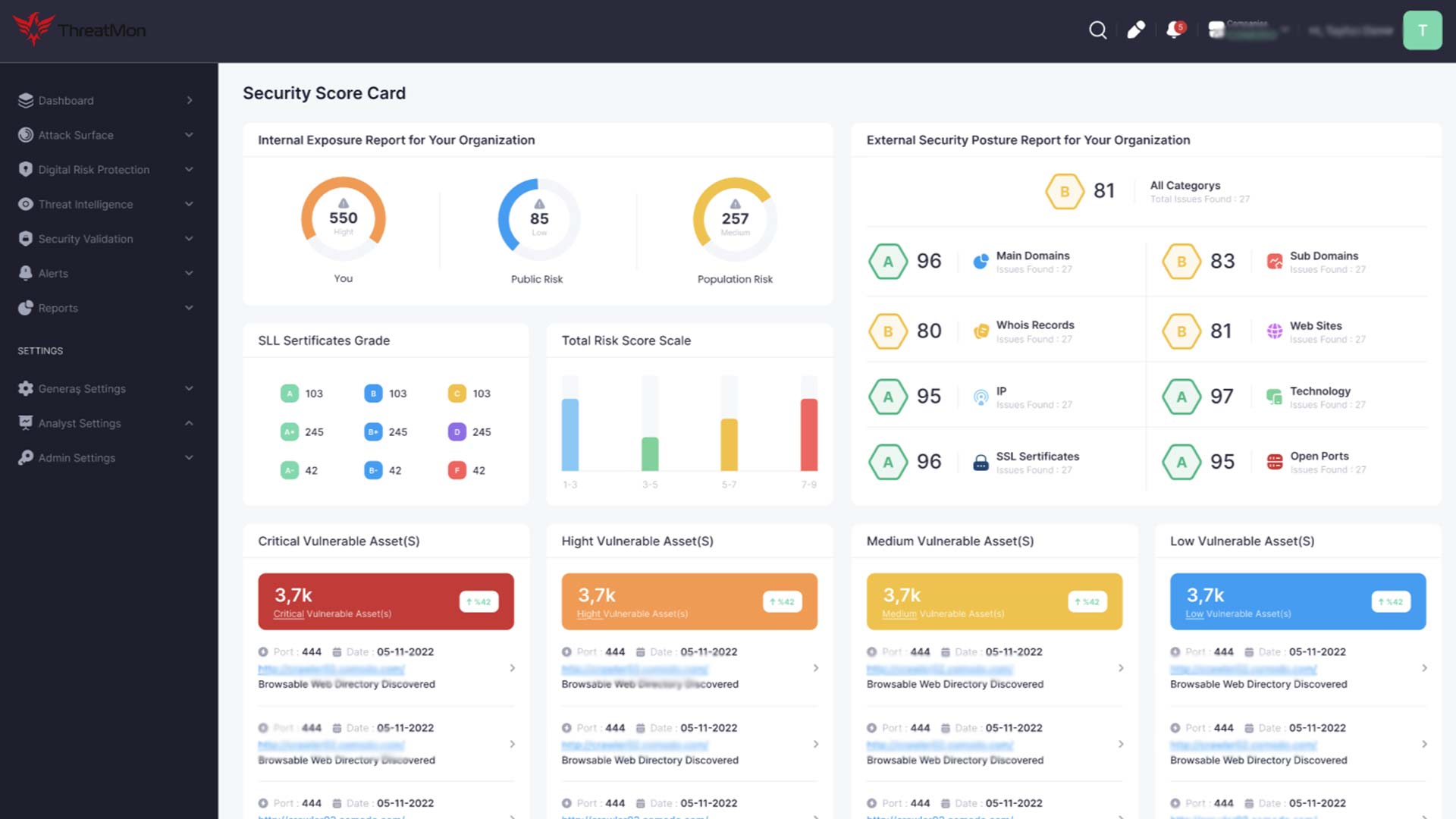
Managing an organization’s External Attack Surface (EASM) brings numerous benefits, enhancing cybersecurity postures, reducing risk, and ensuring operational resilience in the face of evolving digital threats. Here are key benefits that organizations can realize through effective EASM:
Comprehensive Visibility: EASM provides organizations a complete view of their external-facing digital assets, including websites, web applications, APIs, and cloud services. This visibility is crucial for understanding the full scope of potential vulnerabilities and exposures.
Proactive Vulnerability Management: By identifying vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in external assets before attackers can exploit them, EASM enables organizations to address security weaknesses proactively, significantly reducing the likelihood of successful cyber attacks.
Prioritization of Threats: EASM helps organizations prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity and the potential impact on business operations. This prioritization ensures that resources are allocated efficiently to address the most critical issues first.
Enhanced Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: With EASM, organizations can better ensure that their external digital assets comply with relevant cybersecurity regulations and standards, reducing the risk of penalties and legal issues.
Automated Asset Discovery and Management: EASM automates the labor-intensive process of discovering and cataloging external digital assets, freeing IT and security teams to focus on other strategic initiatives.
Integration with Security Ecosystems: Modern EASM solutions integrate seamlessly with existing security tools and workflows, enhancing the overall effectiveness of an organization’s cybersecurity infrastructure.
Support for Digital Transformation: As organizations increasingly adopt cloud services, IoT, and other digital technologies, EASM supports these initiatives by ensuring that new digital exposures are identified and secured promptly.
Protection of Brand Reputation: EASM plays a crucial role in protecting an organization’s reputation and maintaining customer trust by preventing breaches and mitigating vulnerabilities that could lead to data leaks.
Facilitation of Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A): EASM can be instrumental during M&A activities, providing valuable insights into the security posture and potential risks associated with target companies.
Rapid Detection and Response: Continuous monitoring of the external attack surface enables quicker detection of potential threats and vulnerabilities, allowing for a faster and more coordinated response to incidents.
Reduced Impact of Cyber Attacks: By minimizing the window of opportunity for attackers, EASM helps reduce the potential impact of cyber attacks on business operations and sensitive data.
By embracing external attack surface management (EASM), organizations can achieve a more secure, compliant, and resilient operational environment. EASM addresses immediate security concerns and supports long-term strategic business objectives, making it an essential component of modern cybersecurity strategies.
The External Attack Surface Management (EASM) lifecycle outlines a continuous process organizations follow to identify, assess, and mitigate risks associated with their external digital assets. This lifecycle is fundamental for maintaining the security and integrity of an organization’s external-facing technology infrastructure.
The first phase involves identifying and cataloging all external digital assets that an organization owns or is associated with. This includes websites, web applications, cloud services, APIs, and internet-connected devices. The discovery process aims to create a comprehensive inventory of these assets, including known and, importantly, previously unknown or forgotten. Effective discovery requires sophisticated scanning tools that detect assets across various environments and platforms.
Once an inventory is established, each asset is classified based on its criticality and the data it handles. This classification helps prioritize assets for further analysis based on their importance to the business and potential risk. High-value assets that contain sensitive information or are critical to business operations receive higher priority for assessment and protection.
The next step is to conduct thorough vulnerability assessments on the identified assets. This involves scanning for known vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and other security weaknesses that attackers could exploit. The goal is to understand the potential vulnerabilities within the external attack surface and prepare for their remediation.
With the vulnerabilities identified, organizations must analyze the associated risks. This involves evaluating the likelihood of exploitation and the potential impact on the organization should a vulnerability be exploited. Risk analysis helps prioritize vulnerabilities for remediation based on risk level, allowing organizations to allocate resources effectively.
Based on the risk analysis, organizations proceed to remediate the identified vulnerabilities. Remediation might involve applying patches, configuring settings, changing access controls, or even redesigning certain aspects of the system to eliminate vulnerabilities. In cases where immediate remediation is not possible, mitigation strategies may be employed to reduce the risk posed by a vulnerability.
Continuous monitoring of the external attack surface is essential to detect new assets, vulnerabilities, and threats. This phase involves using automated tools to monitor for changes in the attack surface and the emergence of new vulnerabilities or attacks. Reporting is also crucial for documenting the status of the external attack surface, the effectiveness of remediation efforts, and compliance with relevant security standards and regulations.
The EASM lifecycle is iterative, with the final phase focused on reviewing the effectiveness of the management process and implementing improvements. This might involve refining discovery methods, reassessing asset classifications, improving vulnerability assessment techniques, or enhancing remediation strategies. Continuous improvement ensures that the EASM process evolves to address new challenges and adapts to the organization’s external digital footprint changes.
By following this lifecycle, organizations can systematically manage their external attack surfaces, reducing their vulnerability to cyber threats and enhancing their overall security posture. The EASM lifecycle facilitates a proactive approach to cybersecurity, allowing organizations to stay ahead of potential threats and vulnerabilities.
The management of an External Attack Surface (EASM) intersects significantly with privacy and ethics, mainly as organizations increasingly rely on digital platforms and services that handle vast amounts of personal and sensitive data. In this context, EASM is a cybersecurity measure and a critical component of an organization’s commitment to privacy and ethical conduct. Here’s how EASM relates to privacy and ethics:
Organizations are custodians of user data, and their external digital assets often process, store, or transmit this information. As part of the external attack surface, websites, cloud services, and APIs can be vulnerable to cyber attacks that aim to steal or compromise personal data. Ethically, organizations are responsible for protecting this data against unauthorized access or breaches. Effective EASM practices ensure that vulnerabilities in these external assets are identified and mitigated, safeguarding personal data against exploitation and preventing potential privacy violations.
Various international, regional, and local regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and others, impose strict data protection and privacy requirements. Organizations are legally obliged to comply with these regulations, which include ensuring the security of personal data against cyber threats. EASM plays a crucial role in achieving compliance by continuously monitoring and securing external digital assets against vulnerabilities that could lead to data breaches, aligning with ethical and regulatory mandates for privacy protection.
From an ethical standpoint, organizations should be transparent about their data handling practices and measures to protect user data. Effective management of the external attack surface demonstrates a commitment to cybersecurity and data privacy, fostering trust between organizations and their customers, partners, and stakeholders. This trust is fundamental to ethical business practices and can be a significant differentiator in competitive markets.
Ethical hacking, or penetration testing, is a key component of EASM. It involves authorized attempts to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in external assets. This practice must be conducted ethically, respecting privacy and legal boundaries. Furthermore, ethical considerations also apply to vulnerability disclosure. Organizations should have policies for responsibly disclosing discovered vulnerabilities, both in their systems and in those of others, ensuring that such information is shared to minimize the risk of exploitation and facilitate timely remediation.
In their efforts to secure the external attack surface, organizations may employ various monitoring and detection technologies. It’s essential to balance these security measures with privacy considerations, ensuring that monitoring does not infringe on individual privacy rights or collect more data than necessary for security purposes. This balance is crucial for adhering to ethical principles and regulatory requirements related to privacy.
In summary, managing the external attack surface is intrinsically linked to privacy and ethics in the digital age. Organizations must navigate these considerations carefully, implementing robust EASM practices that protect against cyber threats and uphold their ethical responsibilities to protect personal data, comply with regulatory standards, maintain transparency, and foster trust.
The future of External Attack Surface Management (EASM) is set to evolve in response to the dynamic nature of cybersecurity threats and the increasing complexity of digital infrastructures. As organizations expand their digital footprints through cloud adoption, IoT devices, and remote workforces, EASM will become even more critical.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies will play a significant role in automating the detection of vulnerabilities and anomalies within the external attack surface. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential attack vectors, enabling proactive threat mitigation and enhancing the efficiency of security operations.
As more organizations migrate to cloud environments, EASM solutions must offer robust tools for managing cloud-specific vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. Cloud-native EASM features, such as continuous cloud service monitoring and compliance checks, will become standard, ensuring that cloud assets are as secure as on-premise assets.
The interconnected nature of modern business ecosystems means that an organization’s security is often only as strong as that of its weakest link, including third-party vendors and partners. Future EASM solutions will likely incorporate comprehensive third-party risk management capabilities, enabling organizations to assess and manage the risks posed by external parties.
Blockchain technology may be employed within EASM solutions to ensure the integrity and immutability of data related to vulnerabilities, asset inventories, and remediation activities. This can provide a tamper-proof audit trail for compliance purposes and enhance trust in the security data provided by EASM platforms.
As the complexity of external attack surfaces grows, visualization tools will become more sophisticated. These tools will offer intuitive interfaces that allow security teams to quickly understand their organization’s external exposure, prioritize threats, and track remediation efforts. This will enable faster decision-making and more effective communication with stakeholders.
The principles of Zero Trust, which assume that threats can originate from anywhere and that nothing should be trusted implicitly, will become more integrated into EASM strategies. EASM solutions will be key in enforcing Zero Trust policies for external digital assets, ensuring strict verification and least privilege access controls.
As cybersecurity threats evolve, so too will the regulatory landscape. Future EASM solutions must be adaptable to new regulations and compliance requirements, allowing organizations to quickly adjust their security postures and reporting practices to meet changing legal standards.
The future of EASM will likely see increased collaboration between organizations and industries in sharing threat intelligence. Organizations can benefit from a collective defense strategy by pooling resources and information on emerging threats and vulnerabilities, enhancing security for all participants.
As the external attack surface grows and evolves, EASM solutions will adapt and innovate, incorporating new technologies and methodologies to protect organizations from the ever-changing threat landscape. The focus will be on automation, integration, and collaboration, ensuring that security teams can effectively manage external risks and safeguard their digital assets.
As experts at ThreatMon, we highlight critical areas of concern and recommend strategies for organizations to safeguard their external digital assets:
Ransomware attacks represent a significant risk to external assets. To combat this, ThreatMon advises organizations to utilize threat intelligence to conduct analyses specific to their sector and geography. This approach helps identify potential ransomware targets and vulnerabilities within the external attack surface, enabling timely closure of security gaps.
The complexity and effectiveness of cyber attacks are magnified when carried out by organized groups rather than individuals. These groups often comprise members with specialized skills and target an organization’s external digital assets. Organizations need to recognize the collaborative nature of these threats and strengthen their EASM practices accordingly.
The proliferation of botnets and automated malware distribution tools increasingly targets critical infrastructure, large corporations, and small businesses. With advancements in artificial intelligence, these malicious tools are becoming more sophisticated, necessitating advanced EASM solutions capable of detecting and mitigating such automated threats.
The involvement of nation-states in cyber attacks, either directly or through the support of threat actor groups, indicates a trend toward more sophisticated and potentially damaging attacks. This development underscores the importance of robust EASM strategies that can adapt to and counteract state-level cyber espionage and sabotage efforts.
The human element remains a critical vulnerability, with personal credentials, sensitive information, and access to remote systems increasingly compromised and sold online. The widespread adoption of technology further exacerbates this issue, making individuals more susceptible to phishing and other social engineering attacks targeting external assets.
In response to these threats, organizations are urged to adopt comprehensive EASM strategies that include continuous monitoring of the external attack surface, regular vulnerability assessments, and the integration of advanced threat intelligence. By doing so, organizations can better anticipate potential attacks, respond more effectively to emerging threats, and safeguard their critical external digital assets against future cyber threats.
Advancements in External Attack Surface Management (EASM) technologies have significantly transformed how organizations identify, assess, and mitigate vulnerabilities in their external digital assets. These advancements leverage cutting-edge technologies and methodologies to provide more comprehensive, efficient, and automated solutions for securing the external attack surface. Here are some notable developments:
Modern EASM technologies employ advanced scanning and crawling techniques to automatically discover and map all external digital assets associated with an organization. This includes known assets and previously unknown or forgotten assets exposed to the Internet. Automation ensures that the inventory of external assets is always up-to-date, allowing for more effective management and protection.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms are increasingly being used to enhance the detection of vulnerabilities in external assets. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies that indicate security weaknesses, improving the accuracy and speed of vulnerability identification.
With the adoption of cloud computing, EASM solutions have evolved to offer cloud-native security capabilities. These solutions are designed to seamlessly integrate with cloud environments, providing visibility and control over cloud-based assets and services. They can automatically identify misconfigurations, insecure APIs, and other cloud-specific vulnerabilities that could expose an organization to external threats.
EASM technologies increasingly integrate with DevOps practices and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. This integration allows for the early detection and remediation of vulnerabilities in the development lifecycle, ensuring that security is built into applications and services from the outset.
Advanced EASM solutions incorporate threat intelligence and predictive analytics to give organizations insights into emerging threats and vulnerabilities. By analyzing trends and patterns in cyber threats, these solutions can predict potential attack vectors and vulnerabilities before they are exploited, enabling proactive defense measures.
Enhanced risk assessment and prioritization features allow organizations to focus their remediation efforts where they are needed most. EASM technologies can evaluate identified vulnerabilities’ potential impact and exploitability, considering the business context and the criticality of affected assets. This risk-based approach ensures efficient resource use in addressing security weaknesses.
Some EASM platforms incorporate UEBA capabilities to detect anomalous behavior that may indicate a security threat. By monitoring and analyzing user activities and interactions with external assets, UEBA helps identify potential security incidents more quickly and accurately, such as data breaches or unauthorized access attempts.
Blockchain technology is being explored for secure asset management within EASM. By leveraging blockchain’s immutable ledger, organizations can maintain a safe and tamper-proof record of their external digital assets, enhancing the integrity of asset management and vulnerability tracking processes.
These advancements in EASM technologies represent a significant leap forward in organizations’ ability to protect themselves against external cyber threats. By leveraging automation, AI, cloud-native solutions, and integration with DevOps, among other innovations, EASM provides a more dynamic, efficient, and proactive approach to securing the external attack surface.
Selecting an External Attack Surface Management (EASM) platform requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure it meets your organization’s needs and enhances your cybersecurity posture.
Choose a platform that thoroughly discovers all external digital assets, including web applications, APIs, cloud services, and IoT devices. It should identify known and unknown assets, providing complete visibility over your external attack surface.
The platform should excel in detecting a wide range of vulnerabilities and security gaps, offering intelligent prioritization to focus efforts on the most critical issues. This ensures the effective use of resources to mitigate risks.
Ensure the platform integrates seamlessly with your current security infrastructure, including SIEM systems, vulnerability management platforms, and ticketing systems. This will enhance operational efficiency and streamline security workflows.
Look for platforms that automate routine tasks and are scalable to accommodate your organization’s growth. This ensures the platform remains effective as your digital footprint expands.
Opt for a platform that provides real-time monitoring and actionable threat intelligence. This will help you avoid potential threats and make informed decisions about your security strategy.
The platform should support compliance efforts with relevant regulations and offer comprehensive reporting capabilities to effectively communicate risks and actions to stakeholders.
To ensure smooth deployment and utilization, choose a user-friendly platform backed by robust customer support, including training, documentation, and technical assistance.
Consider the vendor’s reputation within the cybersecurity community and look for feedback from other users. A vendor with a strong community and positive testimonials can provide additional value and reassurance.
Focusing on these areas can help you select an EASM platform that effectively secures your external attack surface and aligns with your organization’s cybersecurity objectives.
ThreatMon offers cybersecurity solutions encompassing cyber threat intelligence, attack surface management, and digital risk protection. These solutions are powered by exhaustive data analysis and cutting-edge technological innovation.
Our Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) service is designed to fortify your defenses by providing deep insights into the cybercriminals targeting your organization, including their motivations and tactics. Equipped with continuous monitoring capabilities, this solution delivers real-time alerts on emerging threats, facilitating proactive defense strategies and swift responses. Furthermore, it provides customizable intelligence feeds, allowing a personalized approach to meet your organization’s requirements.
Our Attack Surface Management solution lets you discover and continuously track your organization’s external digital assets. This proactive monitoring alerts you immediately to new vulnerabilities and detects sophisticated anomalies, ensuring your digital presence is secure against evolving cyber threats.
Our Digital Risk Protection offering is geared towards preempting emerging threats and identifying the threat actors behind them. This proactive approach enables organizations to anticipate attacks and implement preventative measures effectively. Continuous threat analysis and monitoring offer a comprehensive understanding of the cyber threat landscape, allowing for informed decision-making and risk mitigation.
With ThreatMon’s Cyber Threat Intelligence Platform, you’re not just informed about vulnerabilities and malicious activities; you’re equipped for rapid intervention, preventing potential damage before it occurs.
ThreatMon excels in External Attack Surface Management (EASM) by providing a comprehensive suite of services designed to identify, assess, and mitigate vulnerabilities across your organization’s external digital footprint. Our approach to EASM includes several key strategies that ensure your digital assets remain secure against evolving cyber threats.
At ThreatMon, we conduct a thorough discovery process to identify all external-facing digital assets associated with your organization. This includes websites, web applications, APIs, cloud services, and internet-connected devices. Our advanced scanning technologies ensure no asset goes unnoticed, providing a complete inventory for effective management.
Utilizing cutting-edge technology, we continuously monitor your external assets for new vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and security gaps. Our system automatically assesses the risk level of each vulnerability, allowing for prioritized remediation based on the potential impact on your organization.
ThreatMon leverages real-time threat intelligence to keep your organization ahead of cybercriminals. By understanding attackers’ latest tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), we can protect your external assets from potential threats and attacks.
We understand that each organization has unique security needs and compliance requirements. ThreatMon works closely with you to develop customized security policies that align with industry standards and regulations, ensuring your external attack surface adheres to best practices and legal obligations.
Our EASM solution incorporates advanced anomaly detection to identify unusual behavior and potential security incidents in real time. This enables swift response to emerging threats, minimizing the risk of compromising your external digital assets.
In the event of a security incident, ThreatMon provides expert incident response and remediation support. Our team of security professionals assists in quickly addressing vulnerabilities, mitigating attacks, restoring normal operations, and minimizing potential damage and downtime.
ThreatMon ensures transparency and accountability through regular reporting and insightful analytics. Our reports detail the status of your external attack surface, highlight security improvements, and recommend further actions to enhance your cybersecurity posture.
By choosing ThreatMon for External Attack Surface Management, you benefit from our expertise, advanced technologies, and customized approach to securing your digital presence. Our commitment to excellence and proactive security measures empower your organization to thrive in a secure and resilient digital environment.
Choosing ThreatMon for your External Attack Surface Management (EASM) has many advantages. It ensures that your organization’s digital assets are comprehensively protected against evolving cyber threats.
ThreatMon is built on specialized knowledge and expertise in managing external digital assets. Our security professionals are dedicated to EASM, staying ahead of the latest threats, technologies, and security practices. Your organization benefits from focused and advanced protection strategies tailored to the unique challenges of securing external attack surfaces.
We invest in state-of-the-art technology and tools designed explicitly for EASM. Our solutions leverage advanced scanning technologies, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) to detect anomalies and vulnerabilities efficiently. With ThreatMon, you gain access to sophisticated EASM capabilities that automate and enhance the security of your external digital assets.
Our services include continuous, around-the-clock monitoring of your external attack surface, ensuring that new vulnerabilities are identified and mitigated promptly. We understand that every organization is unique, so we offer customized solutions tailored to your needs, risk profile, and compliance requirements.
Outsourcing your EASM needs to ThreatMon is a cost-effective solution that allows your internal teams to focus on core business functions without compromising security. Our expertise and specialized tools offer high protection at a fraction of the cost and effort required to develop and maintain similar capabilities in-house.
ThreatMon simplifies navigating the complex landscape of regulatory compliance. Our deep understanding of compliance requirements ensures that your external digital assets adhere to relevant laws and standards, protecting your organization from potential fines and reputational damage.
Proactive Risk Reduction and Incident Response
Our proactive approach to EASM significantly reduces the risk of security breaches and data leaks. Should a security incident occur, ThreatMon is equipped to provide rapid incident response services, minimizing the impact on your operations and guiding you through the recovery process.
ThreatMon’s EASM services can scale as your organization grows and evolves to meet your changing security needs. Whether expanding your digital footprint, entering new markets, or adopting new technologies, we can adjust our services to provide continuous, adequate protection.
Choosing ThreatMon means partnering with an EASM leader committed to protecting your external digital assets through specialized expertise, advanced technology, and tailored, efficient security solutions. Let us help you safeguard your organization against today’s and tomorrow’s cyber threats.